How to Analyze Price Action for Better Trading Decisions
In the fast-paced world of trading, making informed decisions is crucial for success. Price action analysis is a powerful tool that allows traders to interpret market movements based on historical price data. By understanding how prices behave over time, traders can identify trends, reversals, and potential entry and exit points. This article explores the fundamentals of price action analysis, providing insights and techniques that can enhance your decision-making processes in the financial markets.
At its core, price action refers to the movement of a security's price over time. It's like reading the pulse of the market; every tick and fluctuation tells a story about supply and demand dynamics. This section will delve into its significance, emphasizing that price action serves as a foundation for effective trading strategies. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on indicators, price action trading focuses on the actual price movements, making it more intuitive and straightforward. By honing in on price action, traders can gain a clearer understanding of market sentiment and make more precise decisions.
Identifying the essential elements of price action is crucial for any trader. Key indicators, patterns, and trends are the building blocks of price action analysis. Traders should recognize the following components:
- Trends: The direction in which the market is moving—upwards, downwards, or sideways.
- Chart Patterns: Visual formations on charts that signal potential price movements.
- Volume: The number of shares or contracts traded, indicating the strength of price movements.
By understanding these components, traders can better navigate the complexities of the market and make informed decisions.
Support and resistance levels play a vital role in price action analysis. These levels are like invisible barriers that can influence price movements. Support levels act as price floors where buying interest is strong enough to prevent the price from falling further. Conversely, resistance levels serve as price ceilings where selling interest is strong enough to prevent the price from rising. Understanding how to identify these levels is essential for developing effective trading strategies.
To determine support levels, traders often look for historical price points where the price has previously bounced back. Techniques include:
- Analyzing historical price charts for previous lows.
- Using moving averages as dynamic support levels.
- Observing volume spikes at certain price levels.
By pinpointing these support levels, traders can find potential entry points where the price may rebound.
In contrast, identifying resistance levels involves looking for historical price highs. Techniques include:
- Reviewing past price charts for previous highs.
- Utilizing trendlines to visualize resistance.
- Monitoring volume spikes at specific price levels.
Recognizing these resistance levels can help traders determine optimal exit points and manage their risk effectively.
Chart patterns are critical in price action analysis. They provide visual cues about potential future price movements. Some common patterns include:
- Head and Shoulders: Indicates a potential reversal.
- Double Top/Bottom: Signals potential trend reversals.
- Triangles: Suggests continuation or reversal depending on the breakout direction.
Understanding these patterns helps traders anticipate market movements and position themselves accordingly.
Different timeframes can yield varying insights in price action analysis. Whether you are a day trader, swing trader, or long-term investor, choosing the right timeframe is crucial. Short-term analysis can provide quick signals, while long-term analysis offers a broader view of market trends. It's essential to align your trading style with the appropriate timeframe to maximize your effectiveness.
Short-term price action analysis focuses on rapid movements and quick trades, often using 1-minute to 1-hour charts. This approach can yield quick profits but also comes with higher risks due to market volatility. On the other hand, long-term analysis involves daily, weekly, or monthly charts, allowing traders to capture larger trends and reduce the impact of noise in the market. Both approaches have their benefits and drawbacks, and the choice ultimately depends on individual trading goals.
Understanding market psychology is essential for analyzing price action. Trader sentiment can significantly influence price movements. When traders are optimistic, prices tend to rise; conversely, in times of fear, prices may plummet. Recognizing these psychological factors can help traders avoid emotional decision-making and stick to their strategies.
Various indicators reflect market sentiment, such as the Fear and Greed Index and Commitment of Traders (COT) reports. These tools can help traders gauge the overall mood of the market and adjust their strategies accordingly. By staying attuned to market sentiment, traders can enhance their decision-making processes and improve their overall trading performance.
- What is price action trading?
Price action trading involves making decisions based on the movement of price over time, rather than relying on technical indicators. - How do I identify support and resistance levels?
Support and resistance levels can be identified by analyzing historical price points where the price has previously reversed. - What are some common chart patterns?
Common chart patterns include head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and triangles. - Which timeframe should I use for trading?
The choice of timeframe depends on your trading style; short-term traders may prefer 1-minute to 1-hour charts, while long-term traders may use daily or weekly charts.

Understanding Price Action
Price action is a term that refers to the movement of a security's price over time. It’s like the heartbeat of the market, pulsating with the emotions and decisions of traders. Understanding price action is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the often turbulent waters of financial markets. Instead of relying solely on indicators or complex algorithms, price action analysis empowers traders by focusing on the actual price movements themselves. This means that every tick, every spike, and every drop tells a story—one that traders can learn to interpret.
At its core, price action analysis is about recognizing patterns and trends. Think of it as reading the mood of the market; just like you can tell a lot about someone’s feelings by their body language, you can gauge market sentiment through price movements. Traders who master price action can make informed decisions based on how prices have behaved in the past, leading to better predictions about future movements. This approach is not just about numbers; it’s about understanding the psychology behind those numbers.
Moreover, price action serves as a foundation for effective trading strategies. By studying historical price movements, traders can identify key levels of support and resistance, which are critical for determining entry and exit points. These levels act like invisible barriers in the market, where price tends to bounce back or break through. In essence, price action analysis allows traders to develop a keen sense of timing, which is vital for maximizing profits and minimizing losses.
In the world of trading, where uncertainty is the only certainty, price action offers a sense of clarity. It strips away the noise and distractions of various indicators, allowing traders to focus on what truly matters—the price itself. This simplicity can be incredibly powerful. For instance, a trader who understands price action might notice a persistent upward trend and decide to enter a long position, while another trader, relying on lagging indicators, might miss out on that opportunity.
In summary, understanding price action is about more than just numbers; it’s about interpreting the market’s story and using that insight to make informed trading decisions. By honing this skill, traders can enhance their strategies and navigate the markets with greater confidence.

Key Components of Price Action
When it comes to trading, understanding the is like having the secret sauce to a winning recipe. Price action is not just about the numbers you see on a chart; it’s about interpreting those movements and making informed decisions. Think of it as reading the pulse of the market. By focusing on certain indicators, patterns, and trends, traders can better navigate the financial landscape.
One of the most significant aspects of price action is recognizing trends. Trends can be classified into three main categories: upward, downward, and sideways. An upward trend indicates that prices are consistently rising, while a downward trend shows a decline. Sideways trends, on the other hand, represent a period of consolidation where prices move within a range. Understanding these trends is crucial, as they guide traders on when to enter or exit a position.
Another essential component is the identification of key indicators. These indicators serve as signals that can help traders make decisions. For instance, moving averages can smooth out price data to identify the direction of the trend. Similarly, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can indicate whether a security is overbought or oversold, providing insights into potential reversals. By incorporating these indicators into their analysis, traders can enhance their ability to predict future price movements.
Moreover, recognizing chart patterns is vital in price action analysis. Patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops, and flags can signal potential reversals or continuations in price movement. For example, a head and shoulders pattern often indicates that a trend is about to reverse, while a flag pattern suggests a brief consolidation before the trend continues. By mastering these patterns, traders can position themselves advantageously in the market.
To summarize, the key components of price action analysis include:
- Trends: Understanding upward, downward, and sideways trends.
- Indicators: Utilizing tools like moving averages and RSI.
- Chart Patterns: Identifying formations that signal potential market movements.
Incorporating these components into your trading strategy can significantly improve your decision-making process. It’s like having a map in a dense forest; it helps you navigate through the uncertainties of the market with confidence.

Support and Resistance Levels
When diving into the world of trading, understanding is like having a map in uncharted territory. These levels are crucial in price action analysis, acting as psychological barriers where the forces of supply and demand meet. Imagine a game of tug-of-war where one side is trying to pull the price down (sellers) while the other is pushing it up (buyers). This interplay creates zones where price action tends to stall or reverse, making them essential for traders seeking to make informed decisions.
Support levels are essentially the price points at which a security tends to stop falling and may even bounce back up. Think of it as a trampoline; when the price hits this level, it often rebounds, signaling a potential buying opportunity. On the flip side, resistance levels serve as the ceiling that prices struggle to break through. Picture a balloon trying to rise; once it hits the ceiling, it either deflates or falls back down. Recognizing these levels can provide traders with critical insights into when to enter or exit trades.
Identifying these levels isn't just about looking at past price movements; it involves a blend of technical analysis and market psychology. Traders often look for historical price points where the security has reversed direction multiple times. This repetition solidifies these levels in the minds of traders, leading to a self-fulfilling prophecy. Here are some common methods to identify support and resistance levels:
- Historical Price Levels: Check past price charts for areas where the price has bounced or reversed.
- Moving Averages: These can act as dynamic support or resistance levels, especially the 50-day and 200-day moving averages.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Traders often use Fibonacci levels to identify potential support and resistance based on the mathematical ratios derived from the Fibonacci sequence.
Once you've identified these levels, the next step is to watch how the price interacts with them. If the price approaches a support level and shows signs of bouncing back, it could be a signal to buy. Conversely, if it hits a resistance level and starts to decline, it might be time to consider selling. The key is to pay attention to volume; high volume at these levels can indicate stronger support or resistance. Just like a crowd cheering for their team, a surge in volume can reinforce the strength of these price points.
In conclusion, mastering support and resistance levels can significantly enhance your trading strategy. They provide a framework for understanding market dynamics and can help you make more informed decisions. Whether you're a novice or a seasoned trader, integrating these concepts into your analysis can lead to more successful trading outcomes.

Identifying Support Levels
Identifying support levels is a fundamental skill for any trader looking to enhance their price action analysis. Support levels act like a safety net for prices, where they tend to stop falling and often bounce back upwards. Think of it as a trampoline; when the price hits this level, it can rebound, giving traders a potential entry point. But how do you pinpoint these crucial levels? Let’s dive into some effective techniques.
One of the most effective methods for identifying support levels is through the use of historical price data. By analyzing past price movements, traders can spot areas where the price has previously reversed direction. Here are some techniques to consider:
- Previous Lows: Look at historical charts to find points where the price has dipped and then rebounded. These previous lows often serve as strong support levels.
- Moving Averages: Traders often use moving averages as dynamic support levels. For instance, the 50-day or 200-day moving averages can provide insights into where the price might find support.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: This tool helps traders identify potential support levels based on the Fibonacci sequence, which many believe reflects natural market movements.
Moreover, it’s essential to consider the volume at these support levels. High trading volume at a specific price point often indicates that many traders believe that price is a good buy, reinforcing the support. If the price approaches a support level with increasing volume, it’s a strong signal that the level may hold. Conversely, if the price breaks through a support level with high volume, it could indicate a significant shift in market sentiment.
Another important aspect to consider is the timeframe you’re analyzing. Support levels can vary widely between different timeframes. A support level on a daily chart might not hold on a 15-minute chart, so it’s crucial to adjust your analysis based on your trading strategy. For instance, day traders might focus on shorter-term support levels, while swing traders may look for support on daily or weekly charts.
Lastly, always remember that while support levels can provide valuable insights, they are not foolproof. Market conditions can change rapidly, and unexpected news events can lead to price movements that break through established support levels. Therefore, it’s wise to use support levels in conjunction with other indicators and analysis techniques to make well-informed trading decisions.
In summary, identifying support levels is a blend of art and science. By combining historical data analysis, volume checks, and an understanding of market sentiment, traders can better position themselves for potential profits. So, as you prepare for your next trade, keep these techniques in mind and watch for those support levels like a hawk!
- What is a support level? A support level is a price point where a stock or market tends to stop falling and may bounce back upwards.
- How do I identify support levels? You can identify support levels by analyzing historical price data, looking for previous lows, using moving averages, and applying Fibonacci retracement levels.
- Can support levels change? Yes, support levels can change based on market conditions, and they may not always hold during significant market events.
- What should I do if the price breaks through a support level? If the price breaks through a support level, it may indicate a shift in market sentiment, and you should reassess your trading strategy.
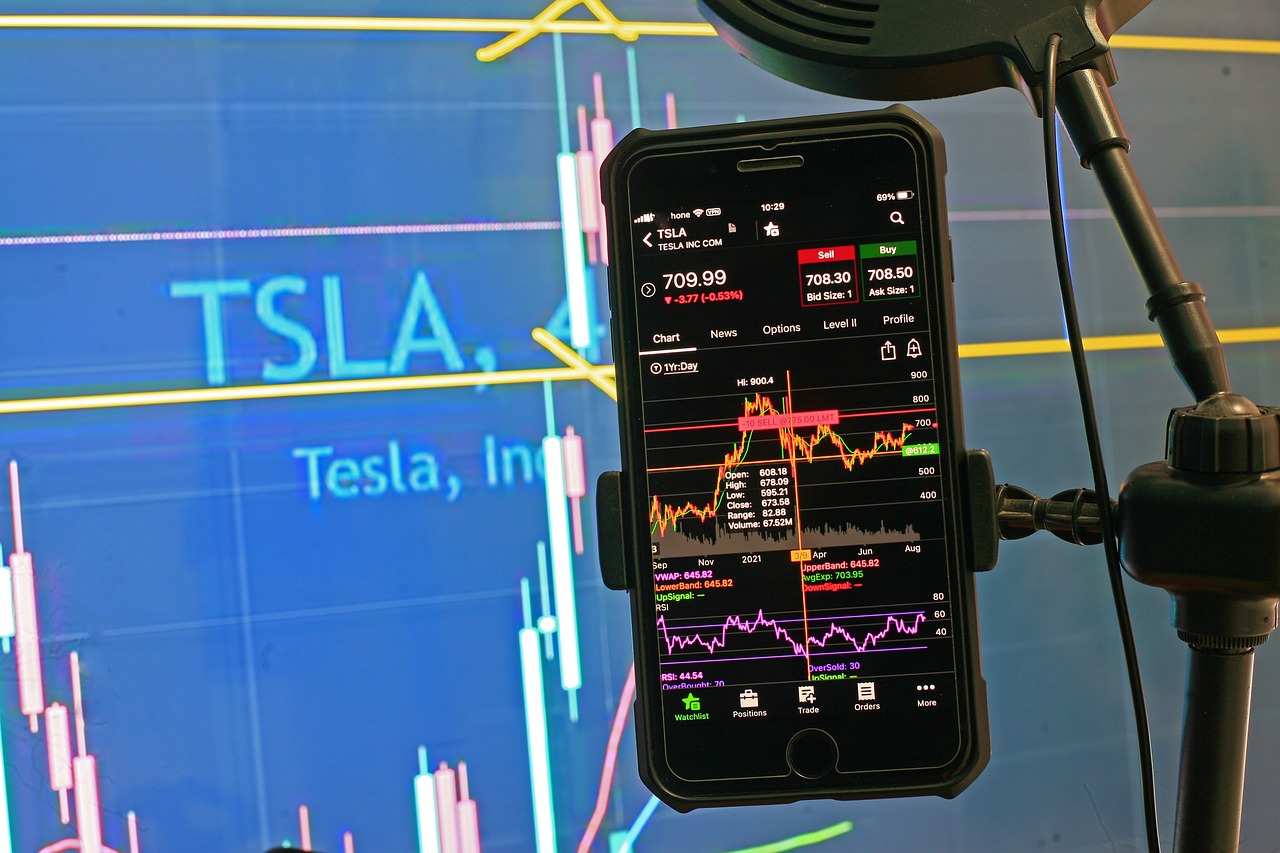
Identifying Resistance Levels
When it comes to trading, identifying resistance levels is akin to finding the ceiling in a room; it’s the point where price struggles to break through. These levels are crucial for traders as they can indicate potential exit points or areas where price reversals might occur. So, how do we pinpoint these elusive resistance levels? It’s all about observing historical price movements and recognizing patterns that have emerged over time.
Resistance levels are typically found at previous highs where selling pressure has overwhelmed buying interest. To effectively identify these levels, traders often look at various timeframes. For instance, a resistance level that appears on a daily chart might not be as significant on a weekly chart. By analyzing multiple timeframes, you can gain a more comprehensive view of the market dynamics at play.
One effective technique for identifying resistance levels is to use horizontal lines on your charts. This involves plotting lines at price points where the asset has previously struggled to rise above. Additionally, traders can utilize technical indicators such as moving averages or Fibonacci retracement levels, which often coincide with resistance zones.
Here’s a simple method to identify resistance levels:
- Historical Highs: Look for price points where the asset has peaked in the past.
- Trend Lines: Draw trend lines connecting previous highs, as these can often indicate future resistance.
- Volume Analysis: High trading volume at a certain price level can suggest strong resistance.
It's essential to note that resistance levels are not set in stone; they can shift over time due to changes in market sentiment or economic conditions. As a trader, you should remain adaptable and continually reassess these levels in light of new information. Moreover, when a resistance level is breached, it can transform into a support level, creating new trading opportunities.
In conclusion, identifying resistance levels is a fundamental skill for any trader looking to enhance their decision-making process. By mastering this technique, you can better navigate the complexities of the market and make more informed trades.
- What is a resistance level? A resistance level is a price point where an asset has historically had difficulty rising above, indicating a potential reversal or pullback.
- How can I identify resistance levels? You can identify resistance levels by analyzing historical price charts, looking for previous highs, and using trend lines and technical indicators.
- What happens when a resistance level is broken? When a resistance level is broken, it can become a new support level, indicating a bullish trend and potential for further price increases.

Chart Patterns and Their Significance
Chart patterns are like the secret language of the market, speaking volumes about potential future price movements. When traders look at a price chart, they aren't just seeing random squiggles; they're witnessing a story unfold. This story, told through various patterns, can help traders make informed decisions. Understanding these patterns is essential for anyone looking to navigate the often turbulent waters of trading.
Common chart patterns include head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, triangles, and flags. Each of these patterns has its own unique implications, and recognizing them can drastically improve a trader's ability to predict market behavior. For instance, the head and shoulders pattern typically signals a reversal in trend, while flags suggest a continuation of the prevailing trend. This means that, depending on the pattern, traders can either prepare to enter a trade or tighten their exit strategies.
Let’s break down some of these patterns:
- Head and Shoulders: Often seen as a reliable reversal pattern, it consists of three peaks: a higher peak (head) between two lower peaks (shoulders). This pattern signals that a bullish trend may be coming to an end.
- Double Tops and Bottoms: These patterns indicate a change in trend direction. A double top occurs after an uptrend and signals a bearish reversal, while a double bottom appears after a downtrend, indicating a potential bullish reversal.
- Triangles: These can be ascending, descending, or symmetrical. They typically indicate a period of consolidation before the price breaks out in either direction, providing traders with potential entry points.
- Flags: Flags are short-term continuation patterns that appear after a strong price movement. They look like small rectangles that slope against the prevailing trend, and their breakout often leads to a continuation of the prior movement.
Recognizing these patterns is not just about memorizing shapes; it's about understanding the psychology behind them. Each pattern reflects the collective sentiment of traders, whether they are feeling bullish or bearish. For example, during the formation of a head and shoulders pattern, the initial enthusiasm (the left shoulder) gives way to a more intense bullish phase (the head), only to be followed by a realization that the trend may be reversing (the right shoulder). This emotional rollercoaster is what creates the patterns we see on our charts.
Moreover, the significance of chart patterns extends beyond mere recognition. Traders often combine these patterns with other technical indicators, such as volume and momentum, to enhance their decision-making process. For instance, a breakout from a triangle pattern accompanied by high volume can be a strong confirmation of a potential price movement. This synergy between chart patterns and other indicators can significantly increase the probability of successful trades.
In conclusion, mastering chart patterns is an essential skill for traders aiming to improve their market analysis. By understanding the significance of these patterns and the psychology behind them, traders can better anticipate price movements and make more informed trading decisions. So, the next time you glance at a chart, remember: it's not just lines and numbers—it's a narrative waiting to be interpreted.
Q1: What is the most reliable chart pattern?
A1: While no chart pattern is foolproof, the head and shoulders pattern is often considered one of the most reliable for predicting trend reversals.
Q2: How can I practice identifying chart patterns?
A2: You can practice by analyzing historical charts and using charting software that allows you to visualize different patterns in real-time.
Q3: Should I rely solely on chart patterns for trading decisions?
A3: It's best to use chart patterns in conjunction with other technical indicators and fundamental analysis to create a well-rounded trading strategy.

Timeframes in Price Action Analysis
When it comes to price action analysis, timeframes are everything. Think of them as the lenses through which you view the market. Each timeframe offers a unique perspective on price movements, allowing traders to make more informed decisions. Whether you're a day trader, swing trader, or long-term investor, understanding how to choose the right timeframe is crucial for your trading success.
Different timeframes can yield varying insights. For instance, a trader looking at a 1-minute chart will see price fluctuations that may not be visible on a daily chart. This can lead to different trading strategies and outcomes. In essence, timeframes help in filtering noise and highlighting significant price movements. But how do you decide which timeframe is best for you?
One effective way to approach this is by considering your trading style and objectives. Here’s a brief breakdown:
- Short-Term Traders: If you thrive on quick trades and fast-paced environments, short-term timeframes like 1-minute or 5-minute charts might be your best bet. These allow you to capitalize on rapid price movements.
- Swing Traders: For those who prefer to hold positions for several days to weeks, daily or 4-hour charts can provide a clearer picture of price trends without the noise of minute-by-minute fluctuations.
- Long-Term Investors: If your focus is on long-term growth, weekly or monthly charts can be invaluable. They help you identify overarching trends and avoid getting caught up in short-term volatility.
It's also worth noting that many traders use multiple timeframes to enhance their analysis. This technique, known as multi-timeframe analysis, involves looking at a higher timeframe to identify the overall trend and then switching to a lower timeframe to pinpoint entry and exit points. This method can significantly improve your trading decisions, as it combines the benefits of both short-term and long-term analysis.
However, it’s essential to recognize the drawbacks of each timeframe. Short-term trading can lead to increased stress and requires constant monitoring of the markets. On the other hand, long-term trading may cause you to miss out on quick opportunities. Finding a balance that suits your personality and lifestyle is key.
In summary, understanding timeframes in price action analysis is not just about choosing one over the other. It’s about integrating various timeframes into your trading strategy to create a comprehensive view of the market. By doing so, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions and enhance your trading performance.
- What is the best timeframe for day trading? Most day traders prefer shorter timeframes, such as 1-minute or 5-minute charts, to capture quick price movements.
- Can I use multiple timeframes simultaneously? Absolutely! Multi-timeframe analysis can provide a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
- How do I know which timeframe suits my trading style? Assess your risk tolerance, time commitment, and trading goals to determine the most suitable timeframe for you.

Short-Term vs. Long-Term Analysis
When it comes to price action analysis, understanding the distinction between short-term and long-term strategies can significantly impact your trading success. Think of short-term analysis as a sprinter in a race, quick and agile, while long-term analysis resembles a marathon runner, steady and enduring. Each approach has its unique advantages and challenges that cater to different trading styles and objectives.
Short-term analysis typically involves trading on smaller timeframes, such as minutes or hours. Traders who favor this method often look to capitalize on rapid price movements, aiming for quick profits. The excitement of short-term trading can be exhilarating, but it also comes with its own set of risks. For instance, the market can be volatile, and unexpected price swings can lead to substantial losses if not managed properly. This is where a keen understanding of price action becomes invaluable.
On the flip side, long-term analysis focuses on broader trends, often spanning days, weeks, or even months. This approach allows traders to ride out short-term fluctuations and benefit from the overall direction of the market. Long-term traders typically rely on fundamental analysis, looking at economic indicators, company performance, and market conditions to inform their decisions. While this method can be less stressful and more forgiving, it requires patience and a strong conviction in one’s analysis, as short-term noise can often lead to second-guessing.
To illustrate the differences further, consider the following table that summarizes key aspects of both approaches:
| Aspect | Short-Term Analysis | Long-Term Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Timeframe | Minutes to hours | Days to months |
| Trading Style | Active and fast-paced | Passive and strategic |
| Profit Goals | Quick, small profits | Large, sustained gains |
| Risk Level | Higher volatility and risk | Lower volatility and risk |
Ultimately, the choice between short-term and long-term analysis boils down to personal preference, risk tolerance, and trading goals. Some traders even adopt a hybrid approach, employing both strategies to diversify their portfolios. This can provide a balance between the thrill of quick trades and the security of long-term investments.
In conclusion, whether you prefer the swift movements of short-term trading or the steady pace of long-term strategies, mastering price action analysis is crucial. It equips you with the tools needed to make informed decisions, regardless of your chosen timeframe. So, which style resonates with you? Are you ready to sprint or are you in it for the long haul?
- What is price action analysis? Price action analysis refers to the study of historical price movements to make trading decisions without relying heavily on indicators.
- How do I choose between short-term and long-term trading? Consider your risk tolerance, time commitment, and trading goals. Experiment with both styles to see which fits you best.
- Can I combine both short-term and long-term strategies? Yes, many traders successfully use a combination of both approaches to diversify their trading tactics.
- What are some common mistakes in price action trading? Common mistakes include ignoring market context, overtrading, and failing to manage risk effectively.

Psychological Aspects of Price Action
When we dive into the world of trading, it’s easy to get lost in the numbers, charts, and indicators. However, one of the most crucial elements that often gets overlooked is the psychological aspect of price action. Why does this matter? Well, understanding market psychology can be the difference between a profitable trade and a costly mistake. Traders are not just robots executing orders; they are human beings influenced by emotions, biases, and collective sentiment.
Every price movement on a chart reflects the decisions of countless traders, each with their own motivations and fears. For instance, when a stock price starts to drop, panic can set in, leading many to sell off their shares, which in turn drives the price down even further. This phenomenon is a classic example of how fear can create a cascading effect in the market. Conversely, when prices rise, greed can take over, prompting traders to buy at inflated prices, often resulting in a market correction.
To navigate these psychological waters effectively, traders must not only analyze price action but also consider the sentiment of the market. This involves looking at various indicators that can provide insights into how traders are feeling at any given moment. For example, the Fear and Greed Index can be a useful tool for gauging overall market sentiment. It ranges from 0 to 100, where values below 50 indicate fear and values above 50 indicate greed. Understanding this sentiment can help traders make more informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
Moreover, it’s essential to recognize that emotions can lead to cognitive biases, which can cloud judgment. Here are a few common biases that traders might encounter:
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to seek out information that confirms one’s existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
- Loss Aversion: The fear of losing money can lead traders to hold onto losing positions for too long, hoping for a turnaround.
- Herd Behavior: Following the crowd can often lead to irrational decision-making, as traders jump on trends without thorough analysis.
Recognizing these biases is the first step toward mitigating their impact. By maintaining a disciplined approach and sticking to a well-defined trading plan, traders can reduce the likelihood of emotional decision-making. Additionally, incorporating risk management techniques can help maintain a level head during volatile market conditions. Setting stop-loss orders and adhering to a predetermined risk-reward ratio can provide a safety net, allowing traders to make decisions based on logic rather than emotion.
In conclusion, the psychological aspects of price action are as vital as the technical elements. By understanding market sentiment and being aware of emotional biases, traders can enhance their decision-making processes. Remember, trading is not just about the charts; it’s about understanding the human element behind every price movement. The more you grasp the psychology of trading, the better equipped you will be to navigate the complexities of the financial markets.
Here are some common questions regarding the psychological aspects of price action:
- What role does trader sentiment play in price action?
Trader sentiment can significantly influence price movements, as collective emotions like fear and greed drive buying and selling decisions. - How can I manage my emotions while trading?
Implementing a solid trading plan, using risk management strategies, and maintaining a disciplined approach can help mitigate emotional decision-making. - What are some tools to gauge market sentiment?
Tools like the Fear and Greed Index, sentiment analysis reports, and social media sentiment can provide insights into how traders are feeling.

Market Sentiment Indicators
When it comes to trading, understanding market sentiment is like having a secret weapon in your arsenal. It gives you insight into how traders feel about a particular asset, which can be a game-changer in your decision-making process. After all, prices don't just move based on fundamentals; they also reflect the collective emotions of the market participants. So, how do you tap into this invaluable resource? That’s where market sentiment indicators come into play.
Market sentiment indicators are tools that help traders gauge the overall mood of the market. These indicators can be categorized into two main types: sentiment surveys and technical indicators. Sentiment surveys involve collecting data from traders and investors about their feelings toward a market or asset. For example, the American Association of Individual Investors (AAII) publishes a weekly sentiment survey that shows the percentage of investors who are bullish, bearish, or neutral about the market. This kind of data can provide a snapshot of the prevailing sentiment and help you make informed decisions.
On the other hand, technical indicators, such as the Fear and Greed Index, serve as a more quantitative approach to measuring market sentiment. This index uses various factors, including volatility, market momentum, and social media sentiment, to provide a score that reflects whether the market is in a state of fear or greed. A high score might indicate over-exuberance, which could signal a potential market correction, while a low score might suggest fear, presenting buying opportunities.
Another interesting aspect of market sentiment is the Commitment of Traders (COT) report. This report provides insights into the positions of various market participants, including commercial traders, non-commercial traders, and retail traders. By analyzing the COT report, you can identify whether traders are leaning heavily in one direction, which can be a precursor to price reversals. For instance, if retail traders are overwhelmingly long on a particular asset while commercial traders are short, it might be a sign of an impending market correction.
To summarize, market sentiment indicators are crucial for any trader looking to enhance their trading strategies. By understanding how other traders feel about the market, you can make more informed decisions and potentially improve your trading outcomes. Here’s a quick look at some key indicators:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Sentiment Surveys | Collect data on trader sentiment, e.g., AAII survey |
| Fear and Greed Index | Measures market sentiment based on various factors |
| Commitment of Traders Report | Shows positions of different market participants |
Incorporating these indicators into your trading routine can help you stay ahead of the curve. Remember, trading is not just about numbers; it's also about understanding the human element behind those numbers. So, keep an eye on market sentiment, and you might just find yourself making better trading decisions.
- What are market sentiment indicators? Market sentiment indicators are tools that help traders gauge the overall mood of the market, reflecting how traders feel about a particular asset.
- How can sentiment surveys help in trading? Sentiment surveys provide insights into the collective feelings of traders, which can indicate potential market movements.
- What is the Fear and Greed Index? The Fear and Greed Index is a tool that measures market sentiment based on various factors, indicating whether the market is in a state of fear or greed.
- Why is the Commitment of Traders report important? The COT report reveals the positions of different market participants, helping traders identify potential reversals in price trends.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is price action analysis?
Price action analysis is a trading technique that focuses on the movement of a security's price over time. It helps traders make decisions based on historical price movements rather than relying on indicators or fundamental analysis. By observing how prices react to different market conditions, traders can identify potential entry and exit points.
-
Why is understanding support and resistance important?
Support and resistance levels are crucial in price action analysis as they indicate where the price tends to reverse or consolidate. Support levels act like a safety net, preventing prices from falling below a certain point, while resistance levels serve as ceilings that prices struggle to break through. Recognizing these levels can help traders make informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
-
How do I identify support and resistance levels?
To identify support and resistance levels, traders can look for historical price points where the price has previously reversed or consolidated. This can be done by analyzing charts and observing where price movements have stalled or bounced back. Additionally, psychological levels, such as round numbers, often serve as significant support or resistance points.
-
What are some common chart patterns to watch for?
Common chart patterns include head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and triangles. Each of these patterns indicates potential future price movements. For example, a head and shoulders pattern often signals a reversal, while triangles can indicate continuation or reversal depending on the breakout direction.
-
How do timeframes affect price action analysis?
Different timeframes can provide varying insights into price action. Short-term analysis focuses on quick trades and can highlight immediate price movements, while long-term analysis looks at broader trends. Choosing the right timeframe depends on your trading style and objectives, as each timeframe can yield different signals and opportunities.
-
What role does market psychology play in price action?
Market psychology significantly influences price action, as trader sentiment can drive price movements. Understanding how emotions like fear and greed impact the market can help traders anticipate price changes. By monitoring market sentiment indicators, traders can adjust their strategies accordingly to align with the prevailing mood of the market.