Understanding the Tax Implications of Crypto Trading
Cryptocurrency trading has taken the financial world by storm, and with its meteoric rise comes a complex web of tax obligations that every trader must navigate. If you've dipped your toes into the crypto waters, you might be wondering: What does all this mean for my taxes? The truth is, the IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property, which can lead to some surprising tax implications. Imagine trading Bitcoin like a stock; every time you buy or sell, you're potentially triggering a taxable event. In this article, we'll break down the intricacies of crypto taxation, ensuring you understand your obligations and can make informed decisions as you navigate this evolving landscape.
First things first, let's get to the core of cryptocurrency taxation. Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies are classified as property by the IRS. This means that every time you sell, exchange, or use your crypto to purchase goods or services, you're engaging in a taxable event. Think of it like selling a piece of art or a collectible; the profit you make is subject to capital gains tax. But don't panic just yet! Understanding these fundamental principles can help you manage your tax obligations effectively. Keeping meticulous records of your transactions is crucial, as you'll need this information when it comes time to report your earnings.
When it comes to crypto trading, understanding the difference between capital gains and ordinary income is vital. Capital gains arise from the sale of an asset, like your beloved Ethereum, while ordinary income is what you earn from your day job or freelance gigs. If you sell your crypto for more than you paid, that profit is considered a capital gain. However, if you receive crypto as payment for services rendered, that income is categorized as ordinary income. This distinction is important because it affects how much tax you owe. For instance, long-term capital gains are typically taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income, which can significantly impact your overall tax liability.
Now, let's dive deeper into the realm of capital gains, specifically the difference between short-term and long-term gains. The duration for which you hold your cryptocurrency before selling it plays a crucial role in determining your tax rate. If you hold an asset for less than a year, any profits are considered short-term capital gains, which are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. On the other hand, long-term capital gains apply to assets held for over a year, typically taxed at a lower rate. This distinction can lead to significant tax savings, so it's worth considering your holding strategy carefully.
So, what exactly constitutes a short-term or long-term holding period? The IRS defines a short-term holding period as any asset held for one year or less, while a long-term holding period is any asset held for more than one year. This means if you buy Bitcoin today and sell it within the next twelve months, any profit you make will be taxed as a short-term capital gain. Conversely, if you hold onto that Bitcoin for over a year before selling, you'll benefit from the lower long-term capital gains tax rate. It's like waiting for a fine wine to age; sometimes, patience pays off in more ways than one!
Now that you understand the differences between short-term and long-term capital gains, let's explore some strategies to minimize your tax burden. One effective method is tax-loss harvesting, where you sell losing investments to offset gains from profitable ones. Additionally, timing your trades strategically can also make a difference. For example, if you anticipate being in a lower tax bracket next year, you might consider delaying the sale of your crypto until then. It’s like playing chess with your finances; every move counts!
When it comes to reporting your crypto transactions, the IRS has specific requirements that you must adhere to. As a trader, you are responsible for reporting every taxable event, which includes sales, exchanges, and even using crypto for purchases. The primary form used for reporting is the IRS Form 8949, where you'll detail your transactions, including the date of acquisition, date of sale, proceeds, and cost basis. It's essential to keep track of these details throughout the year to make tax season less daunting. Remember, failing to report your crypto earnings can lead to hefty penalties, so stay organized!
If you're involved in staking or mining, the tax implications can get even more complicated. Staking rewards, for instance, are considered ordinary income and must be reported in the year they are received. Similarly, mined cryptocurrencies are also taxed as ordinary income at the fair market value on the day you receive them. The complexities of reporting these earnings can be overwhelming, so it's important to stay informed about your obligations. Think of it like navigating a maze; understanding the rules can help you find your way out without getting lost!
Now, let’s clarify what constitutes a taxable event in cryptocurrency trading. A taxable event can occur in several scenarios, including:
- Selling cryptocurrency for cash
- Trading one cryptocurrency for another
- Using cryptocurrency to purchase goods or services
Each of these actions can trigger a tax obligation, so it's crucial to keep detailed records of your transactions to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
As a trader, it’s easy to fall into the trap of common mistakes when it comes to tax reporting. Some frequent errors include failing to report all transactions, misunderstanding holding periods, and neglecting to keep accurate records. To avoid these pitfalls, consider consulting with a tax professional who understands cryptocurrency. This can save you time, stress, and potentially a lot of money in penalties. Remember, knowledge is power, especially when it comes to taxes!
As the world of cryptocurrency continues to evolve, so too will the regulations surrounding taxation. Potential changes in laws and reporting requirements could significantly impact how traders approach their tax obligations. Staying informed about these trends is essential for anyone involved in crypto trading. Think of it as keeping your ear to the ground; being aware of shifts in the landscape can help you adapt and thrive in this dynamic environment.
Q: Do I have to pay taxes on cryptocurrency transactions?
A: Yes, any taxable events related to cryptocurrency, such as selling or trading, must be reported on your tax return.
Q: How do I report cryptocurrency on my taxes?
A: You report cryptocurrency transactions using IRS Form 8949 and the Schedule D of your tax return.
Q: What happens if I don’t report my crypto earnings?
A: Failing to report your earnings can lead to penalties, interest, and potential audits from the IRS.
Q: Are staking rewards considered taxable income?
A: Yes, staking rewards are considered ordinary income and must be reported in the year they are received.

The Basics of Cryptocurrency Taxation
When diving into the world of cryptocurrency, one of the first things you should wrap your head around is how taxation works in this space. It might feel like trying to solve a Rubik's Cube blindfolded, but once you understand the fundamentals, it becomes much more manageable. Essentially, cryptocurrencies are classified as property by the IRS, which means they are subject to capital gains tax just like stocks or real estate. This classification might surprise some, especially those who view cryptocurrencies as a currency. However, this distinction has significant implications for traders and investors alike.
So, what does it mean for you as a trader? Well, every time you sell or exchange your crypto, you're triggering a potential taxable event. This means you need to keep meticulous records of your transactions, including dates, amounts, and the value of the currency at the time of the transaction. It’s like keeping a diary of your crypto adventures—every entry could impact your tax bill!
Moreover, the tax implications can vary significantly based on how you use your cryptocurrency. For instance, if you buy a coffee with Bitcoin, that transaction is taxable. You’re not just spending your Bitcoin; you’re also realizing a capital gain or loss based on the price you paid for that Bitcoin versus its value at the time of the transaction. This can feel overwhelming, but understanding these basics is crucial to avoiding nasty surprises come tax season.
Another aspect to consider is the holding period. The IRS differentiates between short-term and long-term capital gains, which can drastically affect your tax rate. If you hold your cryptocurrency for more than a year before selling, you may qualify for lower long-term capital gains tax rates. This is akin to the difference between a sprint and a marathon; the longer you hold, the better the potential outcome for your tax obligations.
To help you visualize how these factors come into play, here’s a simple table outlining the differences between short-term and long-term capital gains:
| Holding Period | Tax Rate | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Short-Term | Ordinary Income Tax Rates (up to 37%) | Assets held for one year or less |
| Long-Term | 0%, 15%, or 20% (depending on income) | Assets held for more than one year |
In summary, understanding the basics of cryptocurrency taxation is essential for anyone involved in trading. From the classification of cryptocurrencies as property to the nuances of capital gains and holding periods, being informed can save you a lot of headaches down the line. Remember, the more you know, the better equipped you'll be to navigate the sometimes murky waters of crypto taxes!

Capital Gains vs. Ordinary Income
When it comes to cryptocurrency trading, understanding the difference between capital gains and ordinary income is crucial for managing your tax liability. Simply put, capital gains arise from the sale of an asset at a price higher than its purchase price, while ordinary income refers to earnings you receive from regular sources like wages, salaries, or business income. This distinction is particularly important for crypto traders, as the tax implications can vary significantly based on how your profits are classified.
Let's break it down further. Imagine you purchase some Bitcoin for $5,000 and later sell it for $10,000. The $5,000 profit you made is considered a capital gain. However, if you earn income by providing services in exchange for cryptocurrency, that income is categorized as ordinary income. The key takeaway here is that the IRS treats these two types of income differently, which can affect your overall tax rate.
To illustrate this further, let’s consider the tax rates associated with each type of income. Generally, capital gains are taxed at a lower rate compared to ordinary income, especially if they are long-term gains. Here’s a simple comparison:
| Type of Income | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Ordinary Income | 10% - 37% (depends on your income bracket) |
| Short-Term Capital Gains | Same as ordinary income tax rate |
| Long-Term Capital Gains | 0%, 15%, or 20% (depends on your total taxable income) |
As you can see, if you hold your cryptocurrency for more than a year before selling, you may benefit from the reduced long-term capital gains tax rate, which can significantly decrease the amount you owe to the IRS. This is why many traders strategize around their holding periods, aiming to qualify for these lower rates.
Furthermore, it’s essential to note that the duration of your investment plays a pivotal role in determining whether your gains are classified as short-term or long-term. Short-term capital gains apply to assets held for one year or less, which are taxed at your ordinary income rate. In contrast, long-term capital gains apply to assets held for over a year, allowing you to take advantage of those favorable tax rates.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between capital gains and ordinary income is not just a matter of semantics; it can significantly impact your tax bill. As a crypto trader, being aware of how your earnings are categorized will help you make informed decisions about when to sell your assets and how to report your earnings accurately. So, the next time you're contemplating a trade, consider not just the potential profit, but also the tax implications that come along with it!
- What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains? Short-term capital gains apply to assets held for one year or less and are taxed at ordinary income rates, while long-term capital gains apply to assets held for more than a year and are taxed at reduced rates.
- How do I report capital gains from cryptocurrency? You report capital gains on Form 8949 and Schedule D of your tax return, detailing your transactions and the gains or losses incurred.
- Can I offset capital gains with losses? Yes, you can use capital losses to offset capital gains, which can lower your overall tax liability.

Short-Term vs. Long-Term Capital Gains
When it comes to cryptocurrency trading, understanding the distinction between short-term and long-term capital gains can significantly impact your tax obligations. In essence, the duration for which you hold your crypto assets before selling them determines how they are taxed. If you sell your crypto within one year of purchasing it, you're looking at short-term capital gains, which are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. This can lead to a hefty tax bill, especially if you find yourself in a higher tax bracket.
On the flip side, if you hold onto your cryptocurrency for more than a year, you qualify for long-term capital gains treatment. This is where the tax benefits kick in! Long-term capital gains are generally taxed at a lower rate, which can range from 0% to 20%, depending on your overall income. To illustrate this point, let's take a look at a comparison table:
| Holding Period | Tax Rate | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Short-Term (Less than 1 year) | Ordinary Income Tax Rate (up to 37%) | Sold Bitcoin after 6 months at $10,000 profit |
| Long-Term (More than 1 year) | Lower Capital Gains Tax Rate (0% - 20%) | Sold Bitcoin after 18 months at $10,000 profit |
Now, you might be wondering how the IRS defines these holding periods. Essentially, the clock starts ticking the moment you purchase your cryptocurrency. Imagine it like a countdown timer; once it hits one year, you can breathe a little easier knowing you’ll benefit from a lower tax rate. However, it’s crucial to keep meticulous records of your transactions, including the purchase date, sale date, and the prices involved. This diligence will help you prove your holding period in case the IRS comes knocking.
Moreover, there are strategies you can employ to optimize your capital gains tax situation. For instance, if you find yourself in a position where you’ve made substantial profits, consider holding onto your assets for just a bit longer. The difference between a few months can mean a significant reduction in your tax rate. Additionally, if you have losses from other investments, you might think about selling those to offset your gains, a strategy known as tax-loss harvesting.
In summary, the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains in the world of crypto trading is not just a matter of timing; it’s a crucial aspect that can dramatically influence your tax liability. By understanding these concepts and implementing effective strategies, you can navigate the complexities of crypto taxation more effectively and potentially save a considerable amount of money in taxes.
- What is the holding period for capital gains? The holding period is the duration you hold an asset before selling it. Less than one year is short-term, while more than one year is long-term.
- How are capital gains calculated? Capital gains are calculated by subtracting the purchase price from the selling price of the asset.
- Can I offset my capital gains with losses? Yes, you can use losses from other investments to offset your capital gains, which can help reduce your overall tax liability.

Holding Periods Explained
When it comes to cryptocurrency trading, understanding the concept of holding periods is crucial for tax purposes. The holding period refers to the length of time an asset is owned before it is sold or disposed of. In the world of crypto, this can significantly affect your tax liabilities, especially when distinguishing between short-term and long-term capital gains.
So, what’s the difference? In most jurisdictions, including the United States, a short-term capital gain occurs when you sell an asset that you've held for one year or less. This means that any profit you make from trading your cryptocurrency within that timeframe is taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be quite steep. On the other hand, if you hold your crypto for more than one year, you qualify for long-term capital gains treatment, which usually comes with a lower tax rate. This distinction is critical because it can mean the difference between paying a hefty tax bill or enjoying a more favorable rate.
To illustrate this, let's take a look at a simple example:
| Holding Period | Profit | Tax Rate | Tax Owed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Term (1 year or less) | $10,000 | 24% (Ordinary Income) | $2,400 |
| Long-Term (more than 1 year) | $10,000 | 15% (Long-Term Capital Gains) | $1,500 |
As you can see from the table, holding your cryptocurrency for more than a year can lead to significant tax savings. This is why many savvy investors adopt a buy and hold strategy, allowing them to benefit from the lower tax rates associated with long-term capital gains.
However, it’s essential to keep accurate records of your transactions, including the purchase date, sale date, and price at which you bought and sold your crypto. This information is vital for determining your holding period and ensuring you report your taxes correctly. In a fast-paced market like cryptocurrency, it’s easy to lose track of these details, but staying organized can save you from potential headaches come tax season.
In conclusion, understanding holding periods is not just a matter of tax compliance; it’s a strategic component of your overall trading strategy. By being mindful of how long you hold your assets, you can optimize your tax obligations and keep more of your hard-earned gains. So, the next time you consider selling your crypto, take a moment to think about how long you’ve held it—your wallet will thank you!
- What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains? Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates for assets held for one year or less, while long-term capital gains benefit from reduced tax rates for assets held longer than one year.
- How can I keep track of my holding periods? Use a spreadsheet or accounting software to log your transactions, including purchase and sale dates and prices.
- Are there any exceptions to the holding period rules? Some special circumstances may apply, such as specific tax incentives or regulations in your country, so it’s always wise to consult a tax professional.

Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
Minimizing capital gains tax is like navigating a maze; it requires strategy, foresight, and a bit of creativity. As a cryptocurrency trader, you want to keep as much of your hard-earned profits as possible, right? Well, there are several effective methods to achieve this. One of the most popular strategies is tax-loss harvesting. This involves selling off assets that have lost value to offset the gains from those that have appreciated. Imagine it as a balancing act—you're essentially using your losses to cushion the blow of your gains, which can significantly lower your overall tax liability.
Another tactic is to time your trades wisely. If you hold onto your cryptocurrency for more than a year, you qualify for long-term capital gains rates, which are typically lower than short-term rates. Think of it as waiting for the perfect moment to strike; patience can pay off in the form of reduced taxes. Additionally, keeping track of your holding periods is crucial. A simple calendar can help you remember when you bought and sold your assets, ensuring you don’t accidentally fall into the short-term tax trap.
Furthermore, consider your overall income level. If you anticipate a lower income in a future tax year, it might be beneficial to defer selling your assets until then. This strategy can help you take advantage of lower tax brackets. Also, don't overlook the power of donating appreciated assets to charity. Not only do you get to support a good cause, but you also avoid paying capital gains tax on the appreciated value. Plus, you can often deduct the fair market value of the asset from your taxable income, creating a double benefit.
For those who are more adventurous, investing in a self-directed IRA that allows cryptocurrency investments can be a game-changer. This type of retirement account lets you hold cryptocurrencies tax-deferred, meaning you won’t owe taxes on gains until you withdraw funds in retirement. It’s akin to planting a seed that grows tax-free until you're ready to harvest the fruits of your labor.
To wrap things up, the key is to stay informed and proactive. The crypto landscape is constantly evolving, and so are the rules surrounding taxation. Keeping abreast of changes in tax laws and working with a knowledgeable tax professional can help you navigate this complex terrain effectively. Remember, every little bit counts, and by employing these strategies, you can minimize your capital gains tax and keep more of your profits in your pocket.
- What is tax-loss harvesting? Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy where investors sell securities at a loss to offset a capital gains tax liability.
- How long do I need to hold cryptocurrency to benefit from long-term capital gains tax rates? You need to hold your cryptocurrency for more than one year to qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates.
- Can I donate cryptocurrency to charity? Yes, donating cryptocurrency can help you avoid capital gains taxes while allowing you to claim a charitable deduction.
- What is a self-directed IRA? A self-directed IRA is a type of retirement account that allows you to invest in a wider range of assets, including cryptocurrencies, while deferring taxes.

Reporting Requirements for Crypto Transactions
When it comes to trading cryptocurrencies, understanding the reporting requirements is crucial for staying compliant with tax regulations. The IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property, which means that any transaction involving crypto can potentially trigger a tax obligation. This includes not just selling your coins for cash, but also trading one cryptocurrency for another, using crypto to purchase goods or services, and receiving crypto as payment. The key here is that any time you realize a gain or loss, you need to report it.
The primary form used for reporting cryptocurrency transactions is the Form 8949. This form is where you’ll list each of your trades, detailing the date you acquired the asset, the date you sold it, the proceeds from the sale, your cost basis, and the resulting gain or loss. It’s important to keep accurate records of each transaction, including the fair market value of the cryptocurrency at the time of the transaction. This will not only help you when filling out your taxes but also in the event of an audit.
Additionally, you will need to summarize your total gains and losses on Schedule D of your tax return. This is where you’ll report the net gain or loss from all your trades. If you’ve made a profit, this will contribute to your overall taxable income, which can affect your tax bracket and the rate at which you’re taxed. Conversely, if you’ve incurred losses, you can use these to offset gains, potentially lowering your tax liability.
It's also worth mentioning that if you receive cryptocurrency as payment for services or goods, this is considered ordinary income and must be reported as such. The value of the cryptocurrency at the time of receipt is what you will report as income. This can sometimes lead to confusion, especially for those who are new to the crypto space.
To help you navigate the complexities of crypto reporting, here’s a quick overview of some key forms and their purposes:
| Form | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Form 8949 | Report sales and exchanges of capital assets, including cryptocurrency. |
| Schedule D | Summarize your total capital gains and losses. |
| Schedule 1 | Report additional income, including cryptocurrency received as payment. |
Given the rapid evolution of cryptocurrency and its regulations, it’s wise to stay informed about any changes in reporting requirements. The IRS has been increasing its scrutiny of cryptocurrency transactions, so maintaining thorough records and being proactive about compliance can save you from potential headaches down the line. If you're ever in doubt, consulting a tax professional who understands the intricacies of cryptocurrency taxation can provide you with peace of mind.
- Do I need to report every transaction? Yes, any transaction that results in a gain or loss must be reported.
- What happens if I don’t report my crypto transactions? Failing to report can lead to penalties, interest, and potential audits by the IRS.
- Can I use losses to offset gains? Absolutely! You can use capital losses to offset capital gains, which can lower your overall tax liability.
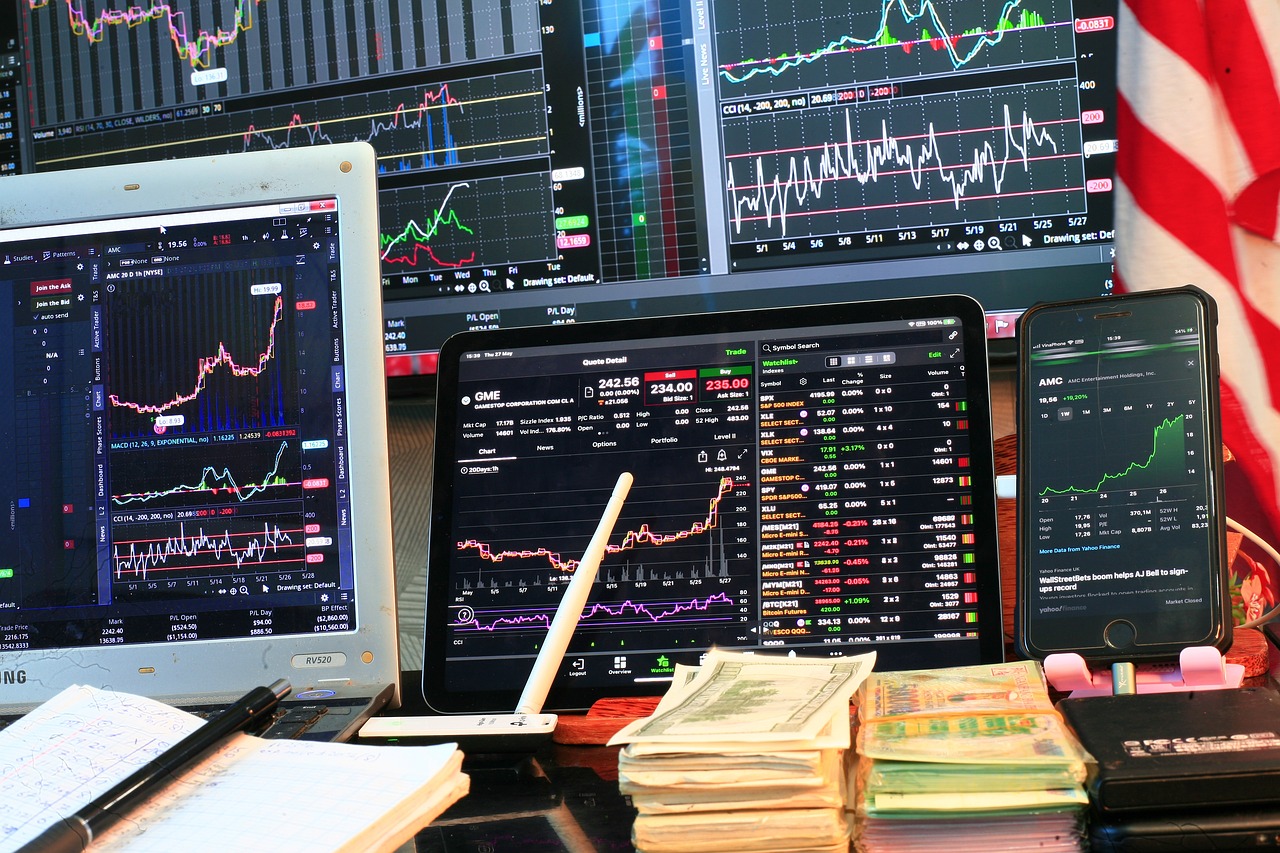

Tax Implications of Staking and Mining
When it comes to the world of cryptocurrency, staking and mining are two popular methods for earning rewards. However, many traders and investors often overlook the tax implications associated with these activities. Understanding how these processes are taxed is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the complex waters of crypto finance. So, what exactly do you need to know about the tax obligations tied to staking and mining?
First off, let’s break down the basics. When you mine cryptocurrencies, you are essentially using computer power to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transactions on the blockchain. In return for this service, miners receive rewards in the form of newly minted coins. Staking, on the other hand, involves holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network. In exchange for this, stakers earn rewards, usually in the form of additional coins. Both of these activities can lead to taxable income.
According to the IRS and many tax authorities around the world, the rewards you earn from both staking and mining are considered ordinary income and should be reported on your tax return. This means that the fair market value of the coins you receive as rewards is taxable at the time you receive them. For example, if you mined or staked 1 ETH when it was valued at $2,000, you would report that $2,000 as income, regardless of whether you later sold that ETH at a higher price.
But wait, there’s more! The tax implications don’t stop at just reporting the income. If you later sell the coins you earned through staking or mining, you may also be responsible for paying capital gains tax on any profits made from that sale. This means you need to keep track of your original cost basis (the value at which you received the coins) and the selling price to determine your gain or loss. This dual taxation can catch many traders off guard, making it essential to maintain accurate records throughout the year.
Now, let’s take a closer look at how to report these activities. It’s not just about knowing that you owe taxes; it’s about understanding the forms and processes involved. Typically, you will need to report your staking and mining rewards on Form 1040 as part of your income. If your total income from these activities exceeds a certain threshold, you may also need to file additional forms, such as Schedule C for self-employment income, depending on your specific situation.
Additionally, it’s important to be aware of the different types of taxable events that can occur in the world of crypto. For instance, if you decide to convert your mined or staked coins into another cryptocurrency or cash them out, this action triggers a taxable event. The IRS requires you to report any gains or losses from these transactions, which can add another layer of complexity to your tax obligations.
To help you better understand the tax implications of staking and mining, here’s a quick overview:
| Activity | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| Mining Rewards | Taxed as ordinary income at the fair market value when received |
| Staking Rewards | Taxed as ordinary income at the fair market value when received |
| Sale of Mined/Staked Coins | Capital gains tax on profit (selling price - cost basis) |
As you can see, the tax implications of staking and mining are multifaceted and can significantly impact your overall tax liability. It's crucial to stay informed and maintain meticulous records of your transactions to ensure compliance with tax regulations. If you’re ever in doubt, consulting with a tax professional who understands cryptocurrency can be a wise investment.
- Do I need to report staking and mining rewards? Yes, both are considered taxable income and must be reported on your tax return.
- How do I calculate my capital gains from crypto sales? Capital gains are calculated by subtracting your cost basis (the value when you received the coins) from the selling price.
- What forms do I need to file for crypto taxes? Typically, you will use Form 1040 and possibly Schedule C, depending on your situation.

Understanding Taxable Events in Crypto
When it comes to cryptocurrency trading, one of the most crucial concepts to grasp is what constitutes a taxable event. Simply put, a taxable event is any activity or transaction that triggers a tax obligation. This is especially important in the world of crypto, where the line between a casual transaction and a taxable event can often be blurry. For instance, did you know that merely exchanging one cryptocurrency for another can be considered a taxable event? That's right! Each time you trade, you may be required to report any gains or losses to the IRS.
To further illustrate this, let’s break down some common taxable events in the realm of cryptocurrency:
- Trading Cryptocurrencies: Whenever you swap one cryptocurrency for another, it’s considered a sale of the first asset, which can lead to capital gains or losses.
- Using Crypto for Purchases: If you use your cryptocurrency to buy goods or services, this is also a taxable event. The IRS views this as selling the crypto for its fair market value at the time of the transaction.
- Receiving Crypto as Income: If you receive cryptocurrency as payment for services or goods, it is treated as ordinary income and taxed at your regular income tax rate.
- Mining and Staking: Rewards earned from mining or staking are considered taxable income at the fair market value of the coins when they are received.
It’s essential to keep track of these events meticulously. The IRS requires taxpayers to report gains and losses for each transaction, which means maintaining accurate records is not just a good practice; it’s a necessity. You may need to calculate the fair market value of your cryptocurrencies at the time of each transaction, which can be a bit of a headache, but it’s vital for compliance.
Another critical aspect to consider is the concept of like-kind exchanges. Historically, some crypto traders believed that exchanging one cryptocurrency for another could be treated as a like-kind exchange, similar to real estate transactions. However, the IRS has clarified that this is not the case, and thus, all crypto trades are subject to capital gains tax. Understanding this distinction is pivotal to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
In summary, recognizing what constitutes a taxable event in cryptocurrency trading is fundamental for every trader and investor. By staying informed and keeping detailed records, you can navigate the complex waters of crypto taxation with greater confidence. Remember, the tax landscape is ever-evolving, and being proactive about your tax obligations can save you from potential headaches down the road.
Q: What is a taxable event in cryptocurrency?
A: A taxable event in cryptocurrency refers to any transaction or activity that triggers a tax obligation, such as trading, using crypto for purchases, or receiving crypto as income.
Q: Do I have to report every crypto transaction?
A: Yes, the IRS requires you to report all taxable events, including trades and purchases, to accurately calculate your gains and losses.
Q: Is exchanging one cryptocurrency for another a taxable event?
A: Yes, trading one cryptocurrency for another is considered a taxable event and may result in capital gains or losses that need to be reported.
Q: How do I calculate the fair market value for my crypto transactions?
A: The fair market value is typically determined by the price of the cryptocurrency at the time of the transaction. You can use various crypto exchanges to find this information.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When it comes to navigating the intricate world of cryptocurrency taxation, even seasoned traders can stumble into pitfalls that could lead to unnecessary headaches come tax season. One of the most prevalent mistakes is failing to keep meticulous records of all transactions. Imagine trying to solve a puzzle without all the pieces—without accurate records, reconstructing your trading history can become a daunting task. Traders should ensure they document every buy, sell, and trade, along with the corresponding dates and amounts. This diligence not only aids in accurate reporting but also provides a safety net in case of an audit.
Another common error is misunderstanding the nature of taxable events. Many traders mistakenly believe that only selling their crypto triggers a taxable event. However, actions such as trading one cryptocurrency for another, using crypto for purchases, or even receiving rewards from staking can also have tax implications. It's essential to recognize that the IRS considers these activities as transactions that may incur capital gains or losses. Therefore, staying informed about what constitutes a taxable event is crucial for compliance.
Moreover, neglecting to report small transactions can lead to significant issues down the line. Some traders might think that if a transaction is minor, it doesn't need to be reported. However, the IRS requires all gains and losses to be reported, regardless of the amount. This oversight could result in penalties and back taxes if discovered. So, remember: no transaction is too small to ignore when it comes to tax reporting.
Many traders also fail to consider the tax implications of holding periods. The difference between short-term and long-term capital gains can be substantial, with short-term gains typically taxed at your ordinary income rate. This is where understanding your holding periods becomes vital. If you find yourself in a position where you're considering selling an asset, it may be worth holding onto it for just a bit longer to benefit from the lower long-term capital gains tax rate.
Finally, one of the most critical mistakes is not seeking professional advice. Cryptocurrency taxation is a rapidly evolving field, and regulations can change at a moment's notice. Consulting with a tax professional who understands the nuances of crypto can provide invaluable guidance, ensuring that you’re not only compliant but also optimizing your tax situation. Remember, it’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to taxes!
- What is a taxable event in cryptocurrency? A taxable event occurs when you sell, trade, or use cryptocurrency in a way that results in a gain or loss. This includes trading one crypto for another or using it to purchase goods or services.
- Do I need to report every transaction? Yes, all transactions need to be reported, regardless of the amount. The IRS requires you to report all gains and losses.
- How can I minimize my capital gains tax? Strategies like tax-loss harvesting, holding assets for over a year, and timing your trades can help minimize capital gains tax.
- Should I consult a tax professional? Yes, it's highly advisable to consult a tax professional, especially if you're actively trading or have complex transactions.

Future Trends in Crypto Taxation
As the world of cryptocurrency continues to evolve, so do the regulations governing it. The future of crypto taxation is a hot topic among traders, investors, and policymakers. The rapid pace of innovation in the crypto space means that tax laws are often playing catch-up, leading to a landscape that is both exciting and complex. So, what can we expect in the coming years? Buckle up, because we are about to dive into the trends that are shaping the future of crypto taxation!
One of the most significant trends is the increased scrutiny from tax authorities. Governments around the globe are recognizing the need to regulate cryptocurrencies, not just for investor protection but also to ensure they collect the taxes owed. For instance, the IRS in the United States has made it clear that cryptocurrency transactions are taxable events, and they are ramping up efforts to enforce compliance. This means that traders should be prepared for more rigorous reporting requirements and potential audits.
Furthermore, we are likely to see a rise in international agreements on crypto taxation. As cryptocurrencies cross borders with ease, countries are beginning to realize that a coordinated approach is essential to prevent tax evasion. Initiatives like the OECD's Global Anti-Base Erosion (GloBE) proposal may pave the way for standardized tax rules for digital assets, which could simplify compliance for traders operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Another trend to watch is the potential for new tax incentives aimed at encouraging innovation in the blockchain space. Some governments are exploring ways to incentivize crypto investments, such as tax breaks for companies that engage in blockchain technology or for individuals who hold cryptocurrencies for extended periods. This could lead to a more favorable environment for crypto enthusiasts, allowing them to thrive while contributing to the economy.
We might also see the emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi) and its impact on taxation. As DeFi platforms gain popularity, the complexities of taxation will increase. For example, how will tax authorities treat yield farming or liquidity mining rewards? The answers are still murky, and it’s likely that new regulations will emerge to address these unique situations. Traders will need to stay informed and adaptable as these developments unfold.
Finally, the integration of technology in tax compliance is on the rise. With the advent of blockchain technology itself, we could see the development of sophisticated tools that help traders track their transactions and calculate their tax liabilities more efficiently. Imagine a world where your crypto wallet automatically generates tax reports based on your trading activity! This could significantly reduce the burden of tax compliance and ensure that traders are accurately reporting their earnings.
In conclusion, the future of crypto taxation is poised for significant changes, driven by regulatory scrutiny, international collaboration, and technological advancements. As a trader, it’s essential to stay ahead of these trends to navigate the evolving landscape effectively. Keep your eyes peeled and your knowledge sharp, because the world of crypto taxation is about to get a lot more interesting!
- What should I do if I missed reporting my crypto transactions? - It's crucial to amend your tax returns as soon as possible. Consult a tax professional for guidance.
- Are there any upcoming regulations I should be aware of? - Yes, keep an eye on announcements from tax authorities and international bodies regarding crypto regulations.
- How can I prepare for future tax obligations related to crypto? - Maintain detailed records of all your transactions and stay informed about tax laws in your jurisdiction.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the tax implications of trading cryptocurrencies?
When you trade cryptocurrencies, you need to be aware that they are classified as property by the IRS. This means any gains or losses from trading are subject to capital gains tax. It's essential to keep track of your transactions to accurately report them on your tax return.
- How do capital gains work in the context of crypto trading?
Capital gains are the profits made from selling an asset. In crypto trading, if you sell your cryptocurrency for more than you paid for it, you incur a capital gain. There are two types: short-term and long-term, which are taxed at different rates depending on how long you've held the asset.
- What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains?
Short-term capital gains apply to assets held for one year or less and are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term capital gains, on the other hand, apply to assets held for more than one year and are typically taxed at a lower rate. Understanding this can save you a significant amount in taxes!
- What constitutes a taxable event in cryptocurrency?
A taxable event occurs when you sell, trade, or use your cryptocurrency in a way that generates income or profit. This includes trading one cryptocurrency for another, selling for cash, or using crypto to purchase goods or services.
- Are there specific reporting requirements for crypto transactions?
Yes, you must report your cryptocurrency transactions on your tax return. This typically involves filling out Form 8949 to report capital gains and losses, along with Schedule D to summarize your overall capital gains. Keeping detailed records of your transactions is crucial for accurate reporting.
- How are staking and mining activities taxed?
Staking and mining are considered taxable events. The rewards you earn from staking or mining are treated as ordinary income, and you must report the fair market value of the rewards at the time you receive them. This can complicate your tax situation, so it's important to stay organized!
- What common mistakes should I avoid when reporting crypto taxes?
Many traders overlook the importance of keeping thorough records, which can lead to underreporting income or miscalculating gains. Additionally, failing to report all transactions can result in penalties. Always double-check your filings and consider consulting a tax professional if you're unsure.
- What future trends should I be aware of regarding crypto taxation?
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency is constantly evolving. Potential changes could include stricter reporting requirements or new tax laws. Staying informed about these trends can help you prepare and adapt your tax strategies accordingly.