The Role of Technical Analysis in High-Frequency Trading
In the fast-paced world of finance, where every millisecond counts, high-frequency trading (HFT) has emerged as a dominant force. But what fuels this lightning-speed trading? One of the key players in this arena is technical analysis, a method that transforms raw market data into actionable insights. By scrutinizing price movements and trading volumes, technical analysis helps traders make informed decisions, ensuring they stay ahead of the curve.
Imagine standing at the edge of a bustling marketplace, where every seller is vying for the attention of buyers. In this scenario, traders are akin to hawkers, calling out their prices and trying to catch the eye of potential customers. Just as a hawker would adjust their offers based on the crowd's behavior, traders use technical analysis to adapt their strategies based on market trends. This analytical approach doesn't just help traders predict price movements; it forms the backbone of their trading strategies in the high-frequency trading landscape.
So, how does technical analysis fit into the intricate puzzle of HFT? Well, it's all about identifying patterns and trends that can signal potential trading opportunities. Traders analyze historical data to uncover price patterns and market trends, which can indicate future movements. This process is similar to reading the weather forecast before planning a picnic; by understanding past conditions, traders can better prepare for what's ahead.
Moreover, the effectiveness of technical analysis in HFT is magnified by the use of sophisticated algorithms. These algorithms process vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling traders to react to market changes almost instantaneously. Think of it as having a supercharged weather app that not only predicts rain but also alerts you the moment a storm is brewing. This level of responsiveness is critical in HFT, where even the slightest delay can result in missed opportunities and significant losses.
As we delve deeper into the methodologies employed in technical analysis, it's essential to highlight the various strategies traders use to navigate the HFT landscape. From market making to arbitrage, each strategy relies heavily on technical analysis to pinpoint optimal entry and exit points. For instance, market makers thrive on providing liquidity, and they utilize technical analysis to determine the best prices at which to buy and sell. This is akin to a skilled negotiator who knows when to push for a better deal based on the current market dynamics.
Arbitrage, on the other hand, exploits price discrepancies across different markets. Here, technical analysis acts as the trader's compass, guiding them swiftly to opportunities that may arise due to fleeting market inefficiencies. Just like a treasure hunter who relies on a map to find hidden gems, traders depend on technical indicators to uncover profitable trades before the window of opportunity closes.
In summary, technical analysis is not just a tool; it's a vital component of the high-frequency trading ecosystem. It empowers traders with the insights needed to make swift, informed decisions in a market where every second matters. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of advanced technical analysis into HFT strategies will likely become even more pronounced, shaping the future of trading as we know it.
- What is high-frequency trading? High-frequency trading (HFT) is a form of algorithmic trading that uses powerful computers to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds.
- How does technical analysis aid in trading? Technical analysis helps traders evaluate securities by analyzing statistics generated from market activity, including price movements and trading volumes.
- What are some common technical indicators? Common indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
- What challenges does technical analysis face in HFT? Challenges include market volatility, data interpretation errors, and the need for continuous adaptation to changing market conditions.

Understanding Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a powerful tool in the world of trading, particularly for those engaged in high-frequency trading (HFT). At its core, technical analysis involves evaluating securities by analyzing statistics generated by market activity. This includes examining price movements, trading volume, and historical data trends. By scrutinizing these elements, traders can make informed decisions about when to enter or exit a trade.
Imagine trying to navigate a dense fog without a map. That’s what trading can feel like without technical analysis. It provides the clarity needed to identify potential opportunities and risks in the market. Traders utilize various charts and indicators to visualize trends and patterns, which can significantly enhance their decision-making process. The beauty of technical analysis lies in its ability to distill complex data into actionable insights.
One of the primary methodologies of technical analysis is the use of charts. These visual representations of price movements can take various forms, including line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts. Each type of chart has its unique strengths. For instance, candlestick charts not only show price movements but also reveal market sentiment through the body and wicks of the candles. This can help traders gauge whether buyers or sellers are in control at any given moment.
Additionally, traders often rely on several key technical indicators to guide their strategies. Some of the most commonly used indicators include:
- Moving Averages: These help smooth out price data to identify trends over a specific period.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): This momentum oscillator measures the speed and change of price movements, indicating overbought or oversold conditions.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): This trend-following momentum indicator shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price.
Understanding how to interpret these indicators is essential for effective technical analysis in HFT. Traders often combine multiple indicators to confirm trends and reduce the chances of false signals. However, it's crucial to remember that technical analysis is not foolproof. Market conditions can change rapidly, and what worked yesterday may not work today. Therefore, traders must remain adaptable and continuously refine their strategies based on real-time data.
In summary, technical analysis serves as a vital component in high-frequency trading by providing traders with the tools they need to analyze market data effectively. By leveraging historical price movements and utilizing various indicators, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve their chances of success in the fast-paced world of trading.

High-Frequency Trading Explained
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a fascinating and complex approach to trading that has transformed the landscape of financial markets. Imagine a world where trades are executed in milliseconds, where algorithms analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, and where traders capitalize on tiny price discrepancies that can vanish in the blink of an eye. That's the essence of HFT. This form of algorithmic trading utilizes powerful computers to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds, allowing traders to take advantage of fleeting market opportunities.
At its core, HFT relies on sophisticated algorithms that process market data and make trading decisions based on statistical models. These algorithms can analyze multiple factors, including price movements, volume, and market sentiment, all at lightning speed. The goal? To outsmart the competition and capture profits from minuscule price changes that traditional traders might miss.
One of the key features of HFT is its reliance on liquidity. By continuously placing buy and sell orders, high-frequency traders provide liquidity to the market, which is essential for maintaining smooth trading operations. In this fast-paced environment, the ability to quickly adjust strategies based on real-time data is crucial. Traders must be able to react almost instantaneously to market fluctuations, which is where technical analysis comes into play.
Technical analysis in HFT is not just about looking at charts; it's about utilizing advanced tools and indicators to make informed decisions. For instance, traders might use algorithms that incorporate technical indicators like moving averages or Bollinger Bands to identify potential entry and exit points. With the right technical analysis, traders can refine their strategies and improve their chances of success.
Moreover, HFT strategies often include a variety of approaches, such as market making, arbitrage, and trend following. Each of these strategies requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and the ability to anticipate price movements. For example, in market making, traders place buy and sell orders to profit from the bid-ask spread. Here, technical analysis helps determine the ideal prices to set for these orders, ensuring that traders can maximize their profits while providing liquidity.
In summary, high-frequency trading is a high-stakes game that blends technology, speed, and strategy. By leveraging technical analysis, traders can navigate the complexities of the market with precision, making split-second decisions that could lead to significant profits. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the role of HFT and technical analysis will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of trading strategies.

Key Strategies in HFT
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a fascinating realm where speed meets strategy. Traders in this space employ a variety of techniques to capitalize on fleeting market opportunities. One of the most prevalent strategies is market making, where firms provide liquidity by continuously placing buy and sell orders. This is akin to being a referee in a fast-paced game, ensuring that the flow of transactions remains smooth. By doing so, they profit from the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the price buyers are willing to pay and the price sellers are asking for.
Another critical strategy is arbitrage. This involves exploiting price discrepancies for the same asset across different markets. Imagine spotting a rare collectible that’s priced lower in one store than another; savvy traders do the same with stocks or commodities. Technical analysis plays a vital role here, as it helps traders quickly identify these discrepancies, allowing them to execute trades before the market corrects itself. The speed of execution in HFT is crucial; missing a moment can mean losing out on potential profits.
Additionally, there’s the trend-following strategy. This is where traders leverage technical indicators to identify and capitalize on market trends. It’s like riding a wave; if you can catch it at the right moment, you can ride it to shore before it crashes. HFT traders often utilize various technical indicators, such as moving averages and momentum oscillators, to make informed decisions on when to enter or exit trades.
To illustrate these strategies further, here’s a brief overview of how they function:
| Strategy | Description | Key Technical Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Market Making | Providing liquidity by placing buy/sell orders to profit from the bid-ask spread. | Order book analysis, bid-ask spread monitoring |
| Arbitrage | Exploiting price differences across different markets. | Price comparison tools, statistical arbitrage models |
| Trend Following | Identifying and capitalizing on market trends. | Moving averages, RSI, MACD |
In conclusion, the key strategies in high-frequency trading are not just about speed; they require a deep understanding of market dynamics and the ability to analyze data swiftly. Each strategy has its nuances, and traders must continuously adapt to the ever-changing market landscape. The integration of technical analysis into these strategies cannot be overstated, as it serves as the backbone for making informed trading decisions in this high-octane environment.
- What is high-frequency trading? High-frequency trading is a form of algorithmic trading that uses powerful computers to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds.
- How does technical analysis benefit HFT? Technical analysis helps traders identify patterns and trends in historical market data, allowing them to make informed trading decisions quickly.
- What are some common technical indicators used in HFT? Common indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
- What challenges do traders face in HFT? Challenges include market volatility, data interpretation errors, and the need for continuous adaptation of strategies.
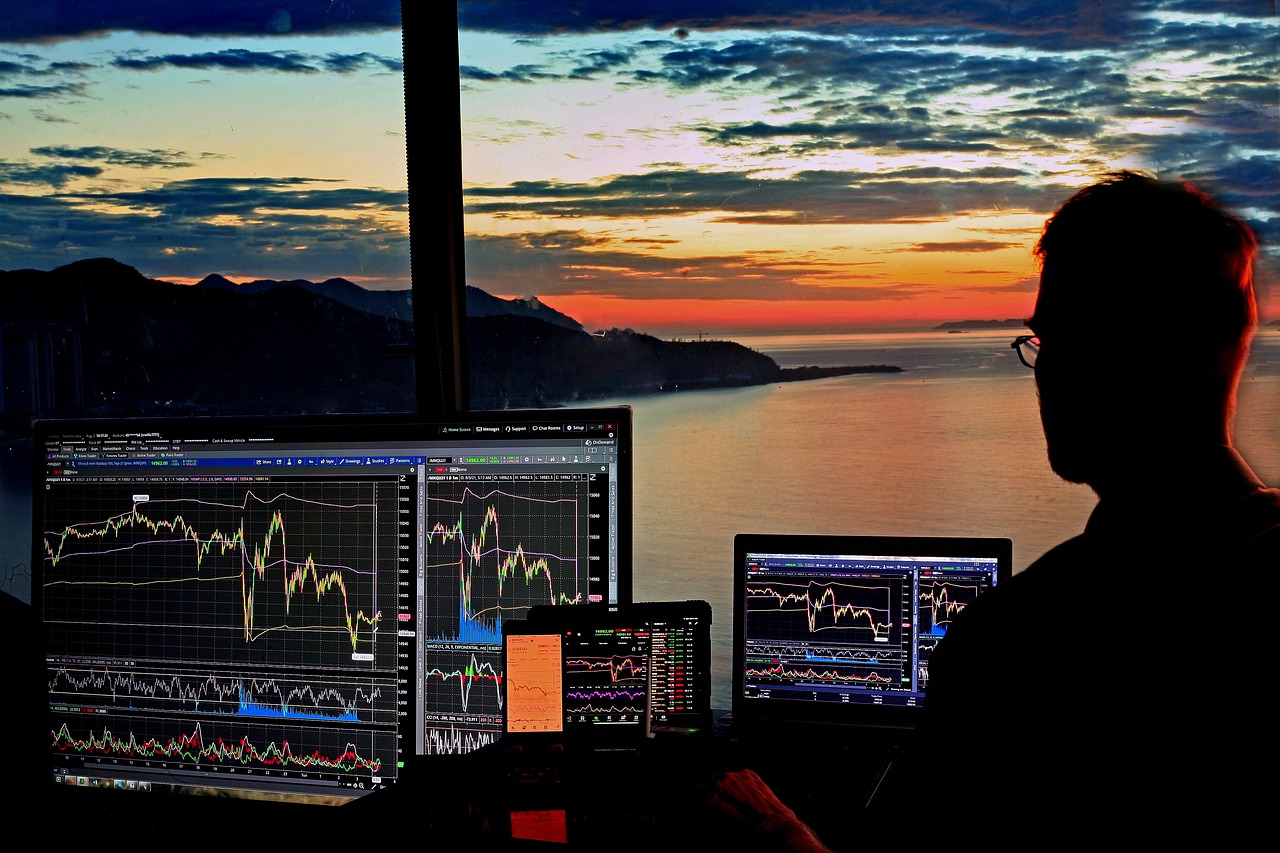

Market Making
Market making is a vital component of high-frequency trading (HFT) that involves providing liquidity to the market by placing simultaneous buy and sell orders. This strategy enables traders to profit from the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the price at which they can buy a security and the price at which they can sell it. In this fast-paced environment, the role of technical analysis becomes indispensable. Traders rely on various technical indicators to determine the optimal prices at which to place their orders, ensuring they can react swiftly to market movements.
Imagine a bustling marketplace where vendors are constantly adjusting their prices based on customer demand and competitor pricing. This is akin to how market makers operate in the financial markets. They must be agile, constantly analyzing data to stay ahead of price fluctuations. Technical analysis provides the tools necessary for this agility, allowing traders to identify patterns and trends that inform their pricing strategies. For instance, a trader might use moving averages to gauge the general direction of a stock's price, helping to inform their buy and sell decisions.
Moreover, the effectiveness of market making is significantly enhanced by the use of algorithms. These algorithms can process vast amounts of data in real-time, executing trades at lightning speed. This capability is crucial, as the window for capitalizing on price discrepancies is often measured in milliseconds. As a result, traders employing market-making strategies must not only have a firm grasp of technical analysis but also leverage technological advancements to maximize their profitability.
In summary, market making is not just about placing orders; it's a complex dance of strategy, timing, and technical analysis. By understanding market dynamics and utilizing the right tools, traders can effectively navigate the challenges of HFT and enhance their chances of success.

Arbitrage Opportunities
Arbitrage opportunities are like hidden treasures in the vast ocean of financial markets. They arise when a security is priced differently in two or more markets, allowing traders to buy low in one market and sell high in another. This price discrepancy is often fleeting, making speed and precision crucial for successful arbitrage trading. In the world of high-frequency trading (HFT), the ability to spot these opportunities quickly can mean the difference between profit and loss, and this is where technical analysis plays a vital role.
Imagine you’re a savvy shopper who knows the best deals in town. You spot a pair of shoes on sale at one store for $50, while the same shoes are selling for $80 at another. If you can grab those shoes before anyone else notices the price difference, you stand to make a quick profit. Similarly, HFT traders use advanced algorithms and technical analysis to identify these fleeting price differences across various exchanges. They capitalize on these opportunities in milliseconds, often before traditional traders even realize what’s happening.
To effectively exploit arbitrage opportunities, traders rely on a mix of technical indicators and real-time data analysis. Some common indicators that assist in identifying these opportunities include:
- Price Action: Monitoring price movements across different markets to spot discrepancies.
- Volume Analysis: Observing trading volumes can help determine the strength of price movements and potential reversals.
- Order Book Depth: Analyzing the order book can reveal where liquidity lies and help traders anticipate price changes.
However, it’s not just about spotting the differences; execution is key. HFT firms deploy sophisticated algorithms that can execute trades in microseconds, ensuring that they can take advantage of arbitrage opportunities before they vanish. These algorithms are designed to analyze vast amounts of data, assess market conditions, and make lightning-fast decisions based on pre-set criteria. Think of it like a race car driver navigating a track; precision, speed, and timing are everything.
Yet, while the prospects of arbitrage trading are enticing, traders must be aware of the inherent risks. Market conditions can change rapidly, and what appears to be a lucrative opportunity can evaporate in an instant. Additionally, transaction costs and slippage can eat into profits, making it essential for traders to factor these elements into their strategies. Thus, a solid understanding of both market dynamics and technical analysis is crucial for anyone looking to dive into the world of arbitrage in HFT.
In conclusion, arbitrage opportunities represent a thrilling aspect of high-frequency trading, where the blend of speed, technology, and technical analysis can lead to substantial profits. As markets continue to evolve, the ability to quickly identify and act on these opportunities will remain a cornerstone of successful trading strategies.
Q: What is arbitrage trading?
A: Arbitrage trading involves buying and selling the same asset in different markets to profit from price discrepancies.
Q: How does technical analysis help in arbitrage trading?
A: Technical analysis provides traders with tools and indicators to identify price movements and trends, helping them spot arbitrage opportunities quickly.
Q: What are some common risks associated with arbitrage trading?
A: Some risks include market volatility, transaction costs, and the potential for execution delays that can affect profitability.
Q: Can individual traders engage in arbitrage trading?
A: While individual traders can engage in arbitrage trading, high-frequency trading typically requires sophisticated technology and algorithms that are more accessible to institutional traders.

Importance of Data Analysis
In the fast-paced world of high-frequency trading (HFT), data analysis is not just important; it is the lifeblood of successful trading strategies. Traders are bombarded with a deluge of information every second, making it essential to sift through this data to identify trends and opportunities. The ability to analyze data quickly and accurately can mean the difference between profit and loss. Imagine trying to catch a fleeting shadow in a dark room; without the right tools and insights, you might miss it entirely.
Data analysis in HFT involves evaluating a wide array of information, including price movements, trading volumes, and market sentiment. Traders utilize sophisticated algorithms and technical analysis tools to process this information efficiently. For instance, moving averages can help smooth out price data, allowing traders to identify potential trends without getting lost in the noise of daily fluctuations. This is akin to using a compass in a dense forest; it helps to navigate through the chaos and find a clear path.
Moreover, the integration of real-time data feeds is crucial for HFT. Traders rely on high-speed internet connections and advanced software to receive and analyze data in real-time. This capability enables them to react to market changes almost instantaneously. To illustrate, consider a scenario where a significant market event occurs, such as a sudden economic announcement. Traders who can analyze the data quickly can capitalize on the resulting price movements before the majority of market participants even have a chance to react.
Furthermore, the importance of data analysis extends beyond mere number crunching. It also involves understanding the context behind the data. For example, a spike in trading volume might indicate a potential trend reversal, but without understanding the underlying reasons—such as news events or changes in market sentiment—traders could misinterpret the signals. Thus, a well-rounded approach to data analysis combines both quantitative and qualitative factors, ensuring that traders make informed decisions.
In addition, the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence in data analysis has revolutionized HFT strategies. These technologies can identify patterns and correlations that may not be immediately apparent to human traders. By leveraging these advanced techniques, traders can refine their strategies and improve their predictive capabilities. However, this also means that traders must stay updated on technological advancements to maintain a competitive edge, as the landscape of HFT is constantly evolving.
To summarize, the role of data analysis in high-frequency trading cannot be overstated. It allows traders to navigate the complexities of the market, identify opportunities, and execute trades with precision. As the trading environment becomes increasingly competitive, those who master the art of data analysis will undoubtedly emerge as the leaders in this dynamic field.
- What is the primary purpose of data analysis in HFT?
Data analysis helps traders identify trends, make informed decisions, and react to market changes quickly. - How do algorithms aid in data analysis?
Algorithms automate the processing of vast amounts of data, allowing for faster and more accurate trading decisions. - What role does machine learning play in HFT?
Machine learning helps identify complex patterns in data, improving predictive accuracy and strategy refinement. - Why is understanding market context important?
Context provides insights into why certain data trends occur, helping traders avoid misinterpretation of signals.

The Impact of Algorithms
In the realm of high-frequency trading (HFT), algorithms are the unsung heroes that drive the engine of modern financial markets. These intricate sets of rules and calculations are designed to automate trading decisions based on technical analysis indicators, enabling traders to react to market changes at lightning speed. Imagine a race car that can make split-second adjustments to its speed and direction, ensuring it stays ahead of the competition. That's how algorithms function in HFT, allowing traders to seize opportunities that would otherwise slip away in the blink of an eye.
Algorithms enhance trading efficiency by processing vast amounts of data in real-time. They analyze price movements, volume, and other market indicators, generating signals that guide trading decisions. This automation not only increases the speed of transactions but also reduces the potential for human error, which can be detrimental in a fast-paced trading environment. The ability to execute trades in milliseconds means that traders can capitalize on fleeting market inefficiencies before they vanish.
However, the impact of algorithms extends beyond mere speed. They also play a crucial role in market liquidity. By continuously placing buy and sell orders, algorithms help maintain a balanced market, ensuring that there are always participants ready to take on trades. This liquidity is vital for the overall health of the market, as it allows for smoother transactions and reduces the likelihood of significant price fluctuations.
To illustrate the power of algorithms in HFT, consider the following table that outlines the key benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Algorithms can execute trades in milliseconds, allowing traders to capitalize on quick market movements. |
| Accuracy | Automated systems minimize human error, leading to more precise trading decisions. |
| Liquidity | Algorithms provide continuous buy and sell orders, enhancing market stability. |
| Data Processing | Algorithms can analyze large datasets quickly, identifying patterns and trends that inform trading strategies. |
Despite these advantages, the reliance on algorithms also brings challenges. For instance, the market can become overly reliant on algorithmic trading, leading to sudden price swings if many algorithms react to the same signals simultaneously. This phenomenon, often referred to as "algorithmic herding," can create volatility and disrupt market equilibrium. Traders must remain vigilant, continuously refining their algorithms to adapt to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, algorithms are a cornerstone of high-frequency trading, enabling traders to make informed decisions in a fast-paced environment. While they enhance speed, accuracy, and market liquidity, traders need to be aware of the potential pitfalls that come with algorithmic trading. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the role of algorithms will undoubtedly remain pivotal in shaping the future of trading.
- What is high-frequency trading?
High-frequency trading is a form of algorithmic trading that uses powerful computers to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds. - How do algorithms improve trading?
Algorithms enhance trading by automating decisions based on technical analysis, increasing speed, accuracy, and market liquidity. - What are the risks associated with algorithmic trading?
Risks include market volatility and the potential for "algorithmic herding," where many algorithms react to the same signals, causing sudden price swings.
Common Technical Indicators
When it comes to high-frequency trading (HFT), understanding technical indicators is crucial for making quick and informed decisions. These indicators act as the compass that guides traders through the turbulent waters of the market, providing insights into price movements and potential trading opportunities. Some of the most commonly used technical indicators include Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
Each of these indicators has its own unique purpose and methodology. For instance, Moving Averages smooth out price data to identify trends over a specific period. This is particularly useful in HFT, where traders need to quickly discern whether a stock is trending upwards or downwards. The two main types of moving averages are the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA). While SMA gives equal weight to all prices, EMA puts more emphasis on recent prices, making it more responsive to new information.
On the other hand, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. This indicator ranges from 0 to 100 and is typically used to identify overbought or oversold conditions in a market. An RSI above 70 often indicates that a security is overbought, while an RSI below 30 suggests it may be oversold. This can be a critical signal for HFT traders who need to act swiftly before market reversals occur.
Another important tool in the HFT arsenal is the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). This indicator helps traders understand the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. The MACD consists of the MACD line, signal line, and histogram, and it can provide insights into potential buy and sell signals. For example, when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it may indicate a bullish trend, prompting traders to buy.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a brief comparison of these indicators:
| Indicator | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Moving Averages | Trend Indicator | Smooths price data to identify trends |
| RSI | Momentum Indicator | Identifies overbought or oversold conditions |
| MACD | Trend & Momentum Indicator | Shows relationship between two moving averages |
In the fast-paced world of HFT, the ability to quickly interpret these indicators can make all the difference. Traders often combine multiple indicators to create a more comprehensive trading strategy. For example, a trader might look for a bullish signal from the MACD while also checking the RSI for confirmation that the stock is not overbought. This layered approach helps traders mitigate risks and improve their chances of success.
However, it's essential to remember that no indicator is foolproof. Market conditions can change rapidly, and relying solely on technical indicators without considering broader market factors can lead to poor decision-making. Therefore, successful HFT traders often integrate these indicators with other forms of analysis, such as fundamental analysis and market sentiment, to create a robust trading strategy.
- What are technical indicators? Technical indicators are statistical tools used to evaluate securities and forecast future price movements based on historical data.
- How do traders use technical indicators in HFT? Traders use technical indicators to identify trends, momentum, and potential reversal points, allowing for quick and informed trading decisions.
- Can technical indicators guarantee profits in HFT? While technical indicators can provide valuable insights, they do not guarantee profits. Market conditions can change rapidly, and successful trading requires a comprehensive strategy.

Challenges in Technical Analysis
While technical analysis is a powerful tool in high-frequency trading (HFT), it is not without its challenges. One major hurdle is the inherent market volatility. Markets can be unpredictable, often influenced by external factors such as economic news, geopolitical events, or sudden shifts in investor sentiment. This volatility can lead to false signals, where a technical indicator suggests a trend that may not hold up under real-world conditions. Traders must remain vigilant and interpret these signals with caution.
Another significant challenge is the quality and accuracy of data. In HFT, traders rely on vast amounts of data to make split-second decisions. However, if the data is flawed or delayed, it can lead to poor trading outcomes. For instance, if a trader bases their strategy on outdated information, they may miss critical market movements, resulting in losses. Therefore, ensuring that data feeds are reliable and up-to-date is crucial for effective technical analysis.
Moreover, interpretation errors can occur even with the best data. Different traders may interpret the same technical indicators in various ways, leading to inconsistent decision-making. For example, one trader might see a bullish signal in a moving average crossover, while another might view it as a false breakout. This subjectivity can create confusion and misalignment in trading strategies, especially in a fast-paced environment like HFT.
Additionally, the increased competition in the HFT space presents another layer of complexity. As more firms enter the market, the strategies that once worked effectively may become less profitable. This saturation can lead to a race for the most advanced algorithms and technology, pushing traders to continuously innovate and adapt their technical analysis methods. In this environment, staying ahead of the curve is essential, but it often requires significant resources and expertise.
Lastly, over-reliance on technical indicators can be detrimental. While these indicators provide valuable insights, they should not be the sole basis for trading decisions. Effective traders often combine technical analysis with fundamental analysis, market sentiment, and other qualitative factors. This holistic approach can help mitigate the risks associated with relying too heavily on any single method.
In summary, while technical analysis is a cornerstone of successful high-frequency trading, it comes with its own set of challenges. Market volatility, data quality, interpretation errors, increased competition, and over-reliance on indicators are all factors that traders must navigate to enhance their trading strategies effectively.
- What is technical analysis? Technical analysis is the study of past market data, primarily price and volume, to forecast future price movements.
- How does technical analysis aid high-frequency trading? It helps traders identify patterns and trends that can be exploited for quick trades, capitalizing on small price discrepancies.
- What are some common technical indicators? Common indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
- What challenges do traders face with technical analysis? Traders face challenges such as market volatility, data accuracy, interpretation errors, increased competition, and over-reliance on indicators.
- Can technical analysis guarantee profits in trading? No, while it can enhance decision-making, it does not guarantee profits due to the unpredictable nature of markets.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is technical analysis in trading?
Technical analysis is the process of evaluating securities by analyzing statistics generated from market activity, such as price movements and trading volume. It helps traders make informed decisions based on historical data trends, allowing them to predict future price movements.
- How does high-frequency trading (HFT) work?
High-frequency trading is a form of algorithmic trading that utilizes powerful computers to execute a large number of orders at incredibly high speeds. HFT takes advantage of small price discrepancies in the market, enabling traders to profit from minute fluctuations in stock prices.
- What are some key strategies used in high-frequency trading?
Some common strategies in HFT include market making, arbitrage, and trend following. Each of these strategies relies on precise execution and robust technical analysis to exploit market inefficiencies effectively.
- What role does technical analysis play in market making?
In market making, technical analysis helps traders identify optimal pricing strategies by assessing market conditions. This allows them to place buy and sell orders that provide liquidity and profit from the bid-ask spread.
- How does arbitrage work in the context of HFT?
Arbitrage in HFT involves exploiting price differences across different markets. Traders use technical analysis to quickly identify these discrepancies, enabling them to execute trades before the opportunity vanishes.
- Why is data analysis crucial in high-frequency trading?
Data analysis is vital in HFT because it allows traders to assess market conditions and refine their strategies. Technical analysis tools help interpret vast amounts of data efficiently, leading to better trading decisions.
- What are common technical indicators used in HFT?
Traders often rely on indicators such as moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to guide their trading decisions. Understanding these indicators is essential for effective technical analysis in HFT.
- What challenges does technical analysis face in HFT?
Despite its advantages, technical analysis in HFT encounters challenges like market volatility and potential data interpretation errors. Traders must continuously adapt their strategies to overcome these obstacles and maintain effectiveness in their trading approaches.