How to Use Technical Indicators to Gauge Market Strength
In the fast-paced world of trading, understanding market strength is crucial for making informed decisions. Technical indicators serve as the compass that guides traders through the turbulent waters of financial markets. They are like the navigational tools of a ship, helping you steer clear of storms and towards profitable shores. By analyzing price movements and trading volume, these indicators can provide valuable insights into market trends and potential future price movements.
Imagine you're a detective, piecing together clues to solve a mystery. Each technical indicator is a clue that, when combined, can reveal the bigger picture of market dynamics. Whether you're a seasoned trader or just dipping your toes into the trading waters, mastering these indicators can significantly enhance your trading strategies. So, let’s dive deeper into the world of technical indicators and discover how they can help you gauge market strength.
Technical indicators are statistical calculations derived from historical price and volume data. Think of them as the metrics that tell you how the market has behaved in the past, allowing you to make educated guesses about its future. They provide insights into market trends, momentum, and volatility, which are essential for traders looking to make informed decisions.
To put it simply, technical indicators act like a magnifying glass, allowing traders to see the underlying patterns and trends that may not be immediately visible. By using these indicators, you can identify entry and exit points, manage risk, and develop a robust trading strategy. But remember, no single indicator is foolproof; they work best when used in conjunction with one another, providing a comprehensive view of market conditions.
There are numerous types of technical indicators, each serving a unique purpose in analyzing market conditions. Broadly, they can be categorized into three main types:
- Trend Indicators: These help traders identify the direction of the market trend.
- Momentum Indicators: These measure the speed of price changes and can signal potential reversals.
- Volatility Indicators: These assess the degree of price fluctuations, helping traders gauge risk.
Understanding these categories is like having a toolbox filled with various instruments, each designed for a specific task. Knowing when and how to use each tool can make a significant difference in your trading outcomes.
Trend indicators are essential for determining the direction in which the market is moving. They help traders understand if the market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or sideways movement. Two popular trend indicators are moving averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX).
Moving averages smooth out price data to identify trends over a specified period. They can be classified into two main types: Simple Moving Averages (SMA) and Exponential Moving Averages (EMA). The SMA calculates the average price over a set number of periods, while the EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information. This responsiveness can be crucial when trying to catch a trend early.
The ADX measures the strength of a trend without indicating its direction. A rising ADX suggests a strong trend, while a falling ADX indicates a weakening trend. This can be incredibly useful for traders looking to determine whether to enter or exit a position based on market strength.
Momentum indicators are like the speedometers of trading; they measure how fast prices are changing. This can help traders identify potential reversals in the market. Two popular momentum indicators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Stochastic Oscillator.
Volatility indicators assess the degree of price fluctuations in the market. Understanding volatility is crucial for managing risk and making informed trading decisions. The Bollinger Bands and the Average True Range (ATR) are widely used volatility indicators.
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (a moving average) and two outer bands that indicate volatility. When the bands expand, it signals increased volatility, while contraction indicates a decrease. Traders often look for price movements that touch or break through the bands as potential trading signals.
The ATR measures market volatility by calculating the average range between high and low prices over a specific period. This information is invaluable for traders when setting stop-loss levels and determining position sizing, ensuring they can manage their risk effectively.
Q: What are technical indicators?
A: Technical indicators are statistical calculations based on historical price and volume data that help traders analyze market trends and make informed decisions.
Q: How do I choose the right technical indicators?
A: The right indicators depend on your trading style and goals. It's often beneficial to use a combination of trend, momentum, and volatility indicators to get a comprehensive view of the market.
Q: Can technical indicators guarantee profits?
A: No, technical indicators are tools that assist in decision-making. They do not guarantee profits, and it's essential to use them alongside other analysis methods and risk management strategies.

Understanding Technical Indicators
When it comes to trading, having a solid grasp of technical indicators can feel like wielding a magic wand. These powerful tools are not just random numbers or lines on a chart; they are statistical calculations derived from historical price and volume data. Think of them as the compass in your trading journey, guiding you through the often turbulent waters of financial markets. They help you decipher market trends and predict potential price movements, thereby enhancing your decision-making prowess.
Technical indicators can be categorized into three main types: trend indicators, momentum indicators, and volatility indicators. Each of these categories serves a unique purpose and can provide valuable insights into market conditions. For instance, trend indicators can help you determine whether the market is on an upward or downward trajectory, while momentum indicators can signal potential reversals in price direction. On the other hand, volatility indicators allow you to assess the level of risk associated with a particular trade.
Let’s break this down a bit further. Imagine you’re trying to navigate through a dense fog. Without the right tools, you could easily lose your way. Similarly, in trading, understanding these indicators allows you to cut through the noise and focus on what truly matters. Here’s a brief overview of the types of technical indicators:
| Type of Indicator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Trend Indicators | Identify the direction of the market trend |
| Momentum Indicators | Measure the speed of price changes and potential reversals |
| Volatility Indicators | Assess the degree of price fluctuations and gauge risk |
In essence, technical indicators are like the dashboard of your car, providing you with essential information to make informed decisions. Just as you wouldn’t drive without checking your speed and fuel levels, you shouldn’t trade without analyzing these indicators. They empower you to make strategic choices, whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out.
As you dive deeper into the world of technical analysis, you’ll discover that these indicators can be used in combination to form a more comprehensive view of the market. For instance, using a trend indicator alongside a momentum indicator can give you a clearer picture of whether to enter or exit a trade. So, buckle up and get ready to explore the fascinating realm of technical indicators, where knowledge truly is power!
- What are technical indicators? Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price and volume data that help traders analyze market trends and make informed decisions.
- Why are technical indicators important? They provide insights into market behavior, helping traders identify trends, potential reversals, and assess risk.
- Can I use multiple indicators at once? Absolutely! Combining different indicators can give you a more nuanced view of the market.
- Are technical indicators foolproof? No, while they are valuable tools, they should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis and good risk management practices.

Types of Technical Indicators
When diving into the world of trading, understanding the various is crucial. These indicators serve as the compass for traders, guiding them through the unpredictable waters of the financial markets. In essence, technical indicators can be categorized into three main types: trend indicators, momentum indicators, and volatility indicators. Each of these categories plays a unique role in helping traders analyze market conditions and make informed decisions.
First up, we have trend indicators. As the name suggests, these indicators are all about identifying the direction of the market trend. They help traders determine whether the market is in an upward, downward, or sideways movement. Some of the most popular trend indicators include moving averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX). By utilizing these indicators, traders can align their strategies with the current market trend, increasing their chances of success.
Next, we move on to momentum indicators. These indicators measure the speed at which prices are changing, allowing traders to identify potential reversals in the market. They act like a speedometer, giving traders insights into whether the market is moving too fast or too slow. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Stochastic Oscillator are two well-known momentum indicators. By keeping an eye on these indicators, traders can spot overbought or oversold conditions, which often precede price reversals.
Lastly, we have volatility indicators. These indicators assess the degree of price fluctuations in the market, which is essential for gauging risk. A market that is highly volatile can lead to significant profits but also poses a greater risk. The Bollinger Bands and the Average True Range (ATR) are widely used volatility indicators. They help traders understand how much the price of an asset might swing, allowing them to set appropriate stop-loss levels and manage their positions effectively.
To sum it up, understanding the different types of technical indicators is fundamental for any trader looking to navigate the complexities of the market. By leveraging trend, momentum, and volatility indicators, traders can gain valuable insights into market dynamics, ultimately enhancing their trading strategies.
Trend Indicators
Trend indicators are essential tools in the trader's arsenal, acting like a compass in the often turbulent seas of the financial markets. They help traders pinpoint the direction of market trends, which is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Imagine trying to navigate a ship without knowing which way the wind is blowing; that's what trading without trend indicators can feel like. By utilizing these indicators, traders can better understand whether to buy, sell, or hold their positions based on the prevailing market conditions.
Two of the most popular trend indicators are Moving Averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX). Each of these indicators serves a unique purpose, yet they complement one another beautifully, much like a perfectly brewed cup of coffee paired with a delightful pastry. Let's delve into these indicators and see how they can enhance your trading strategy.
Moving averages are like the calm after the storm, smoothing out the noise of price fluctuations over a specific period. They help traders identify whether the market is trending upward, downward, or sideways. There are two main types of moving averages: Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The SMA gives equal weight to all prices over a set period, while the EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information.
Here’s a quick comparison of the two:
| Feature | Simple Moving Average (SMA) | Exponential Moving Average (EMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Weighting | Equal weighting | More weight on recent prices |
| Responsiveness | Slower to react | Faster to react |
| Usage | Trend identification | Trend identification and entry/exit signals |
By observing how the price interacts with these moving averages, traders can make educated guesses about future price movements. For instance, if the price consistently stays above the moving average, it may indicate a bullish trend, while prices below the moving average could signal bearish conditions.
The ADX is another powerful trend indicator that measures the strength of a trend without indicating its direction. Think of it as a weather vane that tells you how strong the wind is blowing, but not which way it's blowing. A rising ADX value suggests a strengthening trend, while a falling ADX indicates a weakening trend. Typically, an ADX reading above 25 is considered to indicate a strong trend, while readings below 20 suggest a weak trend.
Using the ADX in conjunction with other indicators can provide a more comprehensive view of market strength. For example, traders might look for an ADX reading above 25 while also confirming the trend direction with a moving average crossover. This combination can help traders avoid false signals and make more informed decisions.
In summary, trend indicators like Moving Averages and the ADX are invaluable tools for traders looking to navigate the complex world of financial markets. By understanding how to use these indicators effectively, you can enhance your trading strategies and increase your chances of success.
- What are trend indicators? Trend indicators are tools that help traders identify the direction of market trends, aiding in making informed trading decisions.
- How do moving averages work? Moving averages smooth out price data over a specific period, helping traders identify trends by observing price interactions with the average.
- What does the ADX measure? The ADX measures the strength of a trend, indicating whether the market is trending strongly or weakly.

Moving Averages
This article explores various technical indicators that traders can use to assess market strength, helping them make informed decisions in their trading strategies.
Technical indicators are statistical calculations based on historical price and volume data. They provide insights into market trends and potential future price movements, aiding traders in their decision-making process.
There are numerous types of technical indicators, including trend indicators, momentum indicators, and volatility indicators. Each serves a unique purpose and can help traders analyze market conditions effectively.
Trend indicators help traders identify the direction of the market trend. Common examples include moving averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX), which signal whether the market is trending upward or downward.
Moving averages are one of the most popular and widely used technical indicators in trading. They work by smoothing out price data over a specific period, allowing traders to identify trends more clearly. Imagine trying to find a clear path in a dense forest; moving averages cut through the noise of daily price fluctuations, helping you see the broader trend. There are two main types of moving averages:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): This is calculated by adding the closing prices of a security over a certain number of periods and then dividing that sum by the number of periods. For example, a 10-day SMA adds the closing prices of the last 10 days and divides by 10.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Unlike the SMA, the EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information. This can be particularly useful in fast-moving markets.
Both types of moving averages can be used to create trading signals. For instance, when the price crosses above the moving average, it may signal a potential buy opportunity, while a cross below could indicate a sell signal. Traders often look for these crossovers as they can signify a shift in market momentum.
Moreover, moving averages can also help in identifying support and resistance levels. When the price approaches a moving average, it might bounce off it, acting as a support level during an uptrend or a resistance level during a downtrend. This ability to act as dynamic support or resistance makes moving averages a crucial tool in any trader's toolkit.
To illustrate the effectiveness of moving averages, let’s take a look at a simple example of a 50-day SMA and a 200-day SMA:
| Date | Closing Price | 50-Day SMA | 200-Day SMA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01-Jan | $100 | $100 | $100 |
| 01-Feb | $105 | $102 | $100 |
| 01-Mar | $110 | $105 | $100 |
| 01-Apr | $120 | $110 | $100 |
| 01-May | $130 | $115 | $100 |
In this example, you can see how the 50-day SMA reacts more quickly to price changes compared to the 200-day SMA. This responsiveness can provide traders with earlier signals, which can be crucial in fast-moving markets.
- What is the best moving average to use? The best moving average depends on your trading strategy. Shorter moving averages (like the 10-day) are better for day trading, while longer ones (like the 200-day) are suited for long-term investing.
- How do I use moving averages in my trading strategy? You can use moving averages to identify trends, generate buy/sell signals, and determine support and resistance levels. Experiment with different periods to find what works best for you.
- Can moving averages be used in all markets? Yes, moving averages can be applied in various markets, including stocks, forex, and commodities. However, always consider the specific characteristics of the market you are trading in.

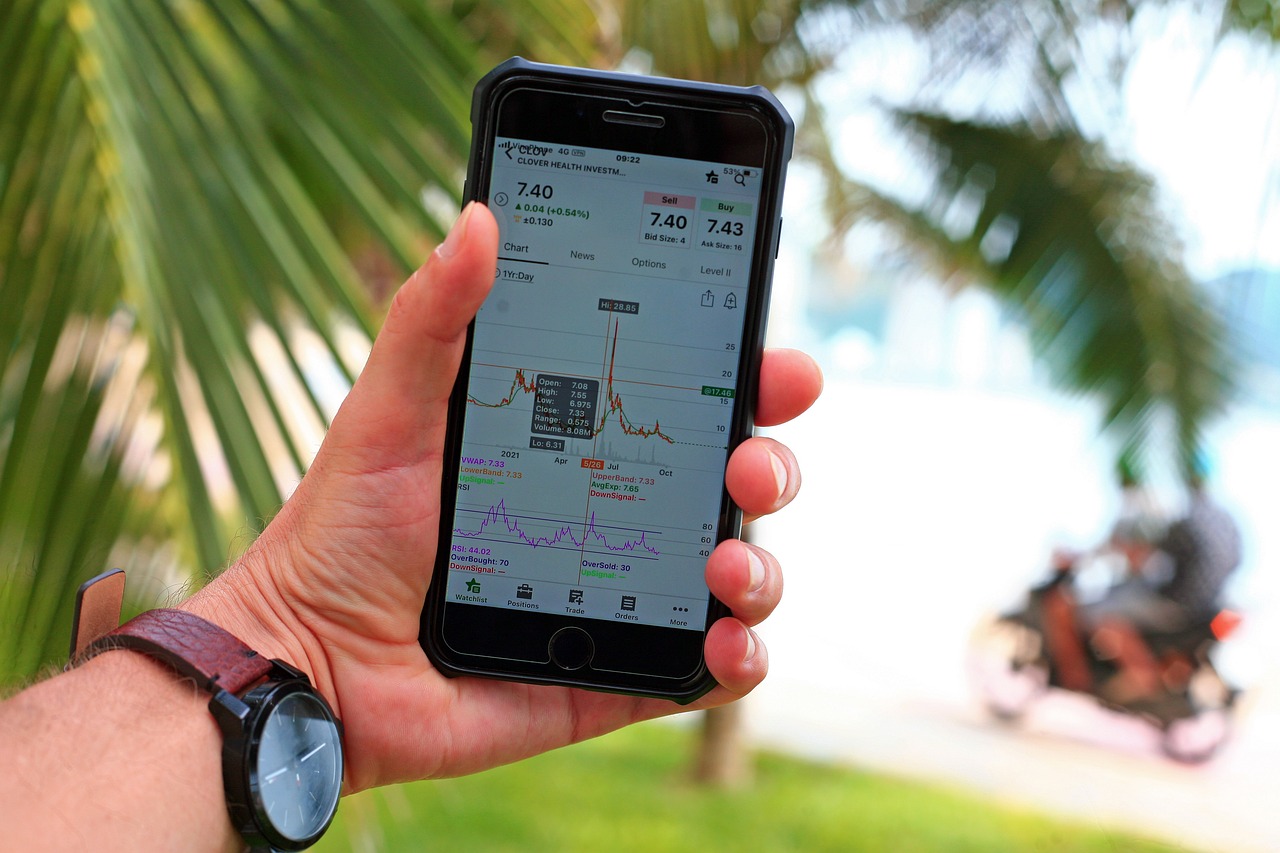
Average Directional Index (ADX)
The is a powerful tool that traders utilize to assess the strength of a trend in the market. Unlike many indicators that tell you the direction of the trend, ADX focuses solely on its strength. This makes it an invaluable asset for traders who want to enter or exit positions based on the intensity of price movements rather than just their direction. Think of ADX as a strength meter; it doesn't tell you if the market is going up or down, but it does tell you how strongly it is moving in that direction.
Typically, the ADX is plotted on a scale from 0 to 100, where values below 20 suggest a weak trend, while values above 20 indicate a stronger trend. Traders often look for specific thresholds to make their trading decisions. For instance, a rising ADX above 20 can signal that a new trend is forming, while a declining ADX below 20 might suggest that the market is entering a consolidation phase. It's essential to remember that a high ADX value doesn't indicate the direction of the trend; it simply shows that the trend is strong, whether it's bullish or bearish.
To clarify how to interpret ADX values, consider the following table:
| ADX Value | Trend Strength |
|---|---|
| 0 - 20 | Weak Trend |
| 20 - 40 | Strong Trend |
| 40 - 60 | Very Strong Trend |
| 60+ | Extremely Strong Trend |
When using ADX, traders often combine it with two other indicators known as the +DI (Positive Directional Indicator) and -DI (Negative Directional Indicator). The interplay between these indicators can provide a more comprehensive view of market conditions. For example, if the +DI is above the -DI while the ADX is rising, it indicates a strong upward trend. Conversely, if the -DI is above the +DI during a rising ADX, it suggests a strong downward trend.
In summary, the Average Directional Index is a critical indicator for assessing trend strength. By understanding how to read its values and combining it with directional indicators, traders can make more informed decisions. Whether you're a seasoned trader or just starting, incorporating ADX into your trading strategy can enhance your ability to navigate the often turbulent waters of the financial markets.
- What does a high ADX value signify? A high ADX value indicates a strong trend, but it does not specify whether the trend is upward or downward.
- Can I use ADX alone for trading decisions? While ADX is useful for gauging trend strength, it is best used in conjunction with other indicators for a more comprehensive analysis.
- What is the ideal ADX value for entering trades? Many traders look for an ADX value above 20 to indicate a strong trend before entering trades.
Momentum Indicators
When it comes to trading, understanding the speed at which prices change can be the difference between riding the wave of profits and getting wiped out by a sudden downturn. This is where come into play. These tools are like a radar for traders, helping them identify potential reversals and gauge the strength of a price movement. Essentially, they measure the rate of change in price, providing insights into whether a security is overbought or oversold. Think of momentum indicators as the pulse of the market, giving traders a sense of how fast the market is moving and in what direction.
Two of the most popular momentum indicators are the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Stochastic Oscillator. Each of these indicators has its unique characteristics and can be used in different trading strategies. The RSI, for example, ranges from 0 to 100 and is typically used to identify overbought or oversold conditions. A reading above 70 often signals that an asset is overbought, while a reading below 30 indicates it may be oversold. This can help traders make informed decisions about when to enter or exit a trade.
On the other hand, the Stochastic Oscillator compares a security's closing price to its price range over a specific period. It generates values between 0 and 100, and similar to the RSI, it helps traders identify potential reversal points. When the Stochastic Oscillator is above 80, it suggests that the asset is overbought, while a reading below 20 indicates it is oversold. By utilizing both the RSI and the Stochastic Oscillator, traders can gain a comprehensive view of market momentum, allowing them to time their trades more effectively.
Here's a quick comparison of these two indicators:
| Indicator | Range | Overbought Level | Oversold Level | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Strength Index (RSI) | 0 - 100 | Above 70 | Below 30 | Identifies overbought/oversold conditions |
| Stochastic Oscillator | 0 - 100 | Above 80 | Below 20 | Compares closing price to price range |
Incorporating momentum indicators into your trading strategy can significantly enhance your ability to make informed decisions. However, it’s crucial to remember that no indicator is foolproof. They should be used in conjunction with other technical analysis tools and fundamental analysis for a well-rounded approach. By blending different indicators, traders can create a more robust trading strategy that not only identifies potential entry and exit points but also manages risk effectively.
- What are momentum indicators?
Momentum indicators are tools used in technical analysis to measure the speed and strength of price movements, helping traders identify potential reversals. - How do I use the Relative Strength Index (RSI)?
The RSI is used to determine overbought or oversold conditions, with readings above 70 indicating overbought and below 30 indicating oversold. - What is the Stochastic Oscillator used for?
The Stochastic Oscillator compares a security's closing price to its price range, helping traders identify potential reversal points based on overbought or oversold levels.

Volatility Indicators
Volatility indicators are essential tools for traders looking to understand market fluctuations. They assess how much the price of an asset varies over a specific period, providing insights into the risk associated with trading that asset. Think of volatility as the heartbeat of the market; when it races, it indicates excitement and potential opportunity, but when it slows, it might signal caution and consolidation. By gauging volatility, traders can make informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
Two of the most popular volatility indicators are Bollinger Bands and the Average True Range (ATR). Each of these indicators provides unique insights into price movements and can help traders navigate the often tumultuous waters of the financial markets.
Bollinger Bands are a dynamic tool that consists of three lines: a middle band, which is typically a simple moving average, and two outer bands that are standard deviations away from the moving average. The outer bands expand and contract based on market volatility. When the market experiences high volatility, the bands widen, indicating potential price movement. Conversely, during low volatility periods, the bands contract, suggesting a possible price breakout or reversal. This makes Bollinger Bands a fantastic tool for identifying entry and exit points in a trade.
Here's a quick overview of how Bollinger Bands work:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Middle Band | Simple moving average (SMA) that represents the trend direction. |
| Upper Band | Middle band + (2 x standard deviation), indicating overbought conditions. |
| Lower Band | Middle band - (2 x standard deviation), indicating oversold conditions. |
The Average True Range (ATR) is another crucial volatility indicator that quantifies market volatility by measuring the average range between the high and low prices over a specified time frame. Unlike Bollinger Bands, which visually represent volatility, the ATR provides a numerical value that traders can use to assess risk. A higher ATR indicates greater price fluctuations, while a lower ATR suggests a more stable market. This information is invaluable for setting stop-loss levels and determining position sizes, as it allows traders to adjust their strategies according to current market conditions.
To put it simply, if you’re looking to navigate the unpredictable seas of the financial markets, understanding volatility indicators like Bollinger Bands and ATR can be your compass. They help you identify when to ride the waves of opportunity and when to anchor down to avoid turbulent waters.
- What are volatility indicators? Volatility indicators are tools used by traders to measure the degree of price fluctuations in the market, helping them gauge risk and make informed trading decisions.
- How do Bollinger Bands work? Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (SMA) and two outer bands that expand or contract based on market volatility, indicating potential price movements.
- What does a high ATR indicate? A high ATR indicates greater price fluctuations, suggesting a more volatile market, which can influence trading strategies.
- Can I use volatility indicators for all types of trading? Yes, volatility indicators can be beneficial for various trading styles, including day trading, swing trading, and long-term investing.

Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a powerful tool in the arsenal of technical indicators, designed to help traders understand market volatility and potential price movements. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, these bands consist of a middle band (which is typically a simple moving average) and two outer bands that are plotted at a set number of standard deviations away from the middle band. This unique setup allows traders to visualize price volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. But how exactly do they work?
The middle band serves as a baseline for the price action, while the upper and lower bands expand and contract based on market volatility. When the market is volatile, the bands widen, indicating a greater potential for price movement. Conversely, when the market is stable, the bands narrow, suggesting lower volatility. This dynamic nature of Bollinger Bands can help traders make informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
One of the key concepts to grasp with Bollinger Bands is the idea of price touching or breaching the bands. Here are a few scenarios to consider:
- Price touching the upper band: This may indicate that the asset is overbought, suggesting a potential reversal or pullback.
- Price touching the lower band: This could signal that the asset is oversold, presenting a buying opportunity.
- Band squeeze: When the bands come close together, it often precedes a significant price movement, either up or down.
Using Bollinger Bands effectively requires a keen understanding of market conditions. For instance, during a strong trend, prices can remain near the upper or lower bands for extended periods. In such cases, traders should be cautious about relying solely on the bands for decision-making. Instead, it's advisable to combine Bollinger Bands with other indicators to confirm signals and enhance trading strategies.
In summary, Bollinger Bands are not just a set of lines on a chart; they are a comprehensive indicator that reflects market conditions and potential price movements. By understanding how to interpret these bands, traders can gain valuable insights into market dynamics and improve their trading outcomes. Whether you're a novice or a seasoned trader, incorporating Bollinger Bands into your analysis can provide a significant edge in the fast-paced world of trading.
What are Bollinger Bands used for?
Bollinger Bands are primarily used to assess market volatility and identify potential overbought or oversold conditions in an asset. They help traders make informed decisions about entry and exit points.
How do I calculate Bollinger Bands?
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines: the middle band (simple moving average), the upper band (middle band + 2 standard deviations), and the lower band (middle band - 2 standard deviations). You can adjust the period and standard deviation settings based on your trading strategy.
Can Bollinger Bands be used in all markets?
Yes, Bollinger Bands can be applied to various financial markets, including stocks, forex, and commodities. However, the effectiveness may vary depending on market conditions and the asset being traded.

Average True Range (ATR)
This article explores various technical indicators that traders can use to assess market strength, helping them make informed decisions in their trading strategies.
Technical indicators are statistical calculations based on historical price and volume data. They provide insights into market trends and potential future price movements, aiding traders in their decision-making process.
There are numerous types of technical indicators, including trend indicators, momentum indicators, and volatility indicators. Each serves a unique purpose and can help traders analyze market conditions effectively.
Trend indicators help traders identify the direction of the market trend. Common examples include moving averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX), which signal whether the market is trending upward or downward.
Moving averages smooth out price data to identify trends over a specific period. They can be simple or exponential, each providing different insights into market behavior.
The ADX quantifies the strength of a trend without indicating its direction. A rising ADX suggests a strong trend, while a falling ADX indicates a weakening trend.
Momentum indicators measure the speed of price changes and help traders identify potential reversals. Popular momentum indicators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Stochastic Oscillator.
Volatility indicators assess the degree of price fluctuations in the market, helping traders gauge risk. The Bollinger Bands and the Average True Range (ATR) are widely used volatility indicators.
The is a vital tool for traders looking to understand market volatility. It measures the average range between high and low prices over a specified period, usually 14 days. By doing so, the ATR provides insights into how much the price of an asset typically moves, which is crucial for setting appropriate stop-loss levels and determining position sizing.
Imagine you're sailing on a boat; the ATR tells you how choppy the waters are. If the waves are high, you know you need to steer carefully to avoid capsizing. Similarly, a higher ATR indicates greater volatility, suggesting that traders should be cautious and possibly adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
One of the most compelling aspects of the ATR is its ability to adapt to changing market conditions. For example, during periods of increased market activity, the ATR will rise, reflecting that the asset is experiencing larger price swings. Conversely, during calmer periods, the ATR will drop, indicating reduced volatility.
To illustrate how ATR can be utilized, consider the following table:
| Period | High Price | Low Price | ATR Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $150 | $145 | $5 |
| 2 | $155 | $148 | $7 |
| 3 | $160 | $150 | $10 |
In this example, as the ATR value increases from $5 to $10, it indicates that the market is becoming more volatile. Traders can use this information to adjust their strategies, perhaps by widening their stop-loss orders to accommodate the increased price swings.
Ultimately, the ATR is not a directional indicator; it doesn’t tell you whether to buy or sell. Rather, it provides a measure of risk. Understanding this can help traders make more informed decisions. So, the next time you're analyzing a market, remember to check the ATR—it could be the difference between a successful trade and a costly mistake!
- What does a high ATR indicate? A high ATR indicates increased volatility, suggesting larger price movements.
- Can ATR be used for all types of assets? Yes, ATR can be applied to stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
- How often should I check the ATR? It’s best to check the ATR regularly, especially when entering or exiting trades.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are technical indicators?
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price and volume data. They help traders analyze market trends and make informed decisions about buying or selling assets.
- How do trend indicators work?
Trend indicators, like moving averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX), identify the direction of the market trend. They help traders understand whether the market is moving upward, downward, or sideways.
- What is the difference between simple and exponential moving averages?
Simple moving averages (SMA) calculate the average price over a specific period, while exponential moving averages (EMA) give more weight to recent prices. This makes EMAs more responsive to price changes, which can be beneficial in fast-moving markets.
- What does the Average Directional Index (ADX) indicate?
The ADX measures the strength of a trend, regardless of its direction. A rising ADX indicates a strong trend, while a falling ADX suggests that the trend is losing momentum.
- What are momentum indicators?
Momentum indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Stochastic Oscillator, help traders gauge the speed of price movements. They can signal potential reversals in market trends, allowing traders to make timely decisions.
- How do Bollinger Bands work?
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (a moving average) and two outer bands that indicate volatility. When the bands expand, it suggests increased volatility, while contraction signals decreased volatility. Traders use this information to anticipate potential price movements.
- What is the Average True Range (ATR)?
The ATR measures market volatility by calculating the average range between high and low prices over a specific period. It is useful for setting stop-loss levels and determining position sizes, helping traders manage their risk effectively.
- Can I rely solely on technical indicators for trading decisions?
While technical indicators are valuable tools, it's essential to combine them with other analysis methods, such as fundamental analysis and market news. This holistic approach helps create a more comprehensive trading strategy.